Share this @internewscast.com
THE viral “Frankenstein bunnies” are eerily similar to an American West phenomenon.
Horned rabbits have recently become an internet sensation, with many likening them to creatures from popular Western legends.
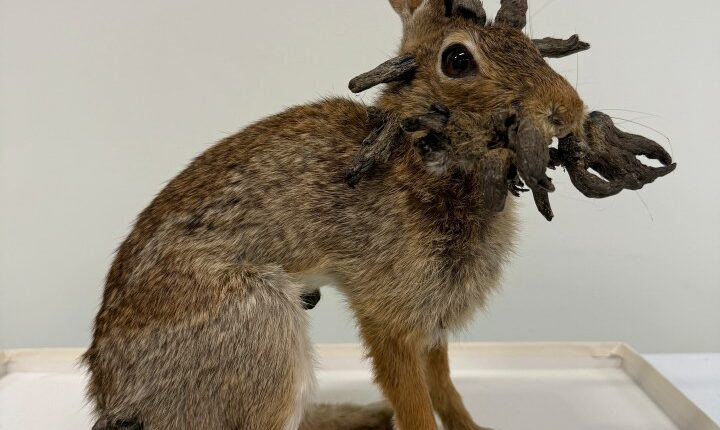
Residents of Fort Collins, Colorado have been told to stay away from the bunnies, which suffer from Shope Papilloma Virus.
The illness causes wart-like tumors on the little animals, and is spread by biting insects.
But some have pointed out that the sick animals look a lot like jackalopes – a rabbit with horns that has become an urban legend.
The Frankenstein-esque creature is simply a jackrabbit body adorned with antelope antlers.
History of the Jackalope
The combination was started by taxidermists in Douglas, Wyoming, during the 1930s.
Douglas Herrick, alongside his brother, Ralph, came back from hunting one day and threw a jackrabbit body on the ground next to deer horns.
The brothers put the two things together and there, a jackalope was born.
Similar to myths such as Bigfoot, the Loch Ness Monster, and the Jersey Devil, there’s ongoing debate about whether these animals are genuinely found in nature.
Stories of these creatures vary widely, describing them as “killer” rabbits or attributing them the ability to imitate human voices, allegedly including singing alongside cowboys by the fireside.
They also have a “fondness for whiskey,” according to the Douglas, Wyoming, website.
The town, where the infamous animal originated, has since taken the jackalope and turned it into a cultural phenomenon.
Douglas is adorned with symbols of these creatures: there are statues at the visitor center, a “thirteen-foot cutout” on a hillside at the city’s edge, and the creature is even on the town’s emblem.
The town’s website describes these antlered animals as resembling jackrabbits but astonishingly able to run at speeds of up to 90 miles per hour.
“Their rarity is ensured by the fact that they only breed during lightning flashes.”
What Is Shope Papilloma Virus?
- A viral disease causing wart-like tumors on rabbits, mainly on their heads, ears, and eyelids.
- Spread by biting insects like mosquitoes and ticks.
- Tumors can be benign or turn malignant (cancerous).
- Commonly affects wild and pet rabbits, especially during summer and fall.
- Treatment usually involves surgical removal of growths.
- Prevention focuses on protecting rabbits from insect bites
Visitors can buy a hunting license for the mythical beings, and street signs tell drivers to watch out for wild jackalope roaming the roads.
Surprisingly, you can even buy “jackalope milk.”
The site also claims their milk, naturally homogenized by their strong jumps, possesses remarkable aphrodisiac qualities and a variety of healing properties.
“However, the females can only be milked when lulled into sleeping belly up, generally as a result of a whiskey induced stupor.”
Douglas, Wyoming, has mentioned the bunny sickness that has taken the internet by storm in recent weeks may be confused with the creature’s origin, but says those who believe it’s the virus have an “inferior imagination.”
“While the traveler is unlikely to have the opportunity to have an actual sighting of the rare and ferocious jackalope, they will witness its strong impact on the community,” it wrote.
“We embrace the wild and independent nature of the jackalope, and welcome visitors to share in the fun.”