Share this @internewscast.com

LEVELLAND, Texas (AP) — A group of scientists is embarking on a unique mission, chasing storms to gather fresh hail. They’re putting themselves and their vehicles at risk, enduring the dents caused by hail, all in the pursuit of knowledge. They believe the hailstones hold valuable insights about storm behavior, the damage they can cause, and possibly even about the atmospheric conditions.
But what do you do with nearly 4,000 melting iceballs?
A lot.
These researchers are part of the pioneering Project ICECHIP, focused on studying hail. They are examining the hailstones by measuring their size, weight, and structure, cutting them open, crushing them, and cooling them. They transport them across multiple states to uncover the mysteries within. Occasionally, out of sheer interest and amusement, they even taste the hailstones.
The main goal is to understand “what the hailstone was doing when it was in the storm,” explained Victor Gensini, a lead scientist and meteorology professor at Northern Illinois University.
Calipers and crushers
It’s pushing midnight on a Friday in a Texas Walmart parking lot, and at least 10 vans full of students and full-time scientists are gathering after several hours of rigorous storm chasing. Hailstones are in coolers in most of these vehicles, and now it’s time to put them to the test.
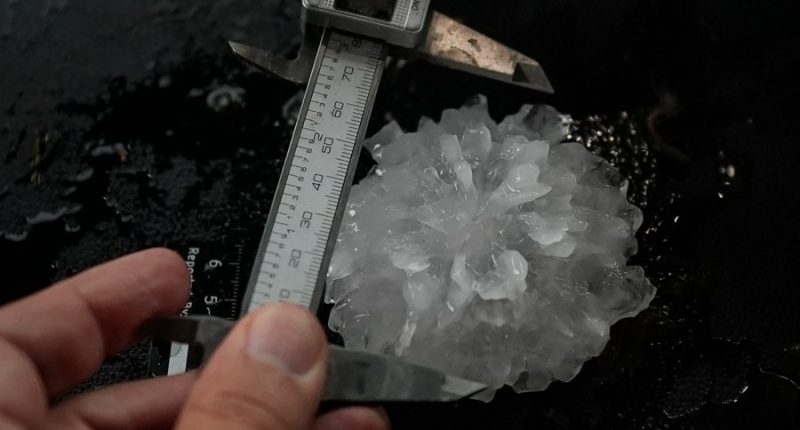
Researchers use calipers to measure the width, in millimeters, of the hailstones, which are then weighed. So far after more than 13 storms, the biggest they found is 139 millimeters (5.5 inches), the size of a DVD. But on this night they are smaller than golf balls.
Once the measurements are recorded in a laptop, the fun starts in the back of a van with a shark-festooned beach blanket protecting the floor.
The hail is put on a vertical device’s white holder. Jake Sorber, a meteorologist at the Insurance Institute for Business and Home Safety, squeezes a hand grip about a foot above it and another white block comes crashing down, crushing the ice to smithereens. In the front of the van, Ian Giammanco, another IBHS meteorologist, records how much force it took to cause the destruction.
“That tells us about its strength,” Giammanco said.
Different teams do this over and over, with the debris littering vans. It’s all about trying to get good statistics on how strong the typical hailstone is. On this night, Gaimmanco and colleagues are finding the day’s hail is unusually soft. It’s surprising, but there’s a good theory on what’s happening.
“In hailstones we have layers. So we start off with an embryo, and then you’ve got different growth layers,” said Central Michigan University scientist John Allen. “That white growth is what’s called dry growth. So basically it’s so cold that it’s like super cold liquid water freezing on surface. … All the gas gets trapped inside. So there’s lots of air bubbles. They tend to make a weak stone.”
But don’t get used to it. Less cold air from climate change could conceivably mean harder hail in the future, but more research is needed to see if that’s the case, Giammanco said.
“Damage from a hailstone is not just dependent on how fast and the exact amount of energy it has. It’s how strong are these hailstones,″ Giammanco said. ”So a really soft one is not actually going to damage your roof very much, especially an asphalt shingle roof. But a really strong one may crack and tear that asphalt shingle pretty easily.”
How to collect a pristine hailstone
Mostly researchers grab hail to test after it falls, wearing gloves so as not to warm or taint the ice balls too much.
But to collect pristine hail and get it cold as soon as possible, there’s SUMHO, a Super Mobile Hail Observatory. It’s a chest-high metal funnel that catches hail and slides it directly down into a cooler. No contamination, no warming.
Most of these pristine hailstones go directly to a cold lab in Colorado, where they are sliced with a hot wire band saw. The different layers — like a tree’s rings — will help scientists learn about the short but rapid growth of the ice in the storm, Gensini said.
Scientists will also figure out what’s in the hail besides water. Past research has found fungi, bacteria, peat moss and microplastics, all of which helps researchers know a bit more about what’s in the air that we don’t see.
After weeks of collecting these ice balls, Central Michigan student Sam Baron sampled the fruit of his labors.
“It tastes like an ice cube,” Baron said. “It’s like the good ice that they serve at restaurants.”
___
The Associated Press’ climate and environmental coverage receives financial support from multiple private foundations. AP is solely responsible for all content. Find AP’s standards for working with philanthropies, a list of supporters and funded coverage areas at AP.org.