Share this @internewscast.com
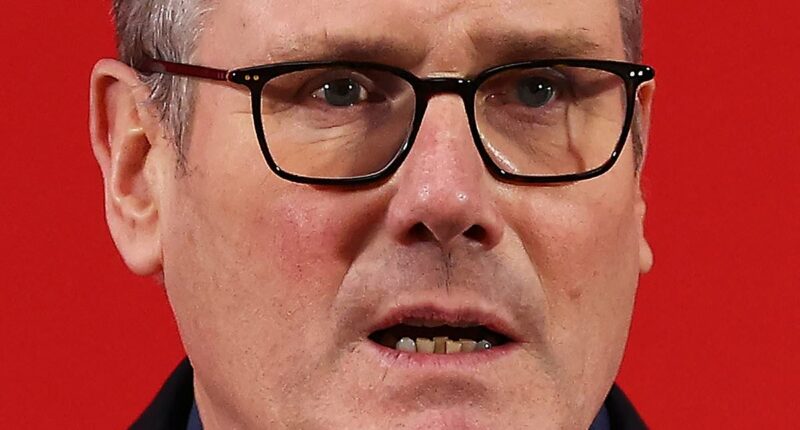
Labour MPs are calling for Keir Starmer to relinquish his role and allow a temporary prime minister to take charge until a leadership contest can be organized in the summer.
Disillusioned members of the Government’s backbench warn that if the Prime Minister doesn’t step down amidst the Peter Mandelson controversy, the party may face severe losses in the upcoming Gorton and Denton by-election, potentially followed by a disastrous outcome in May’s local elections.
There is optimism among these MPs that the Cabinet might convince Sir Keir to resign this week, paving the way for a neutral candidate like Defence Secretary John Healey or Northern Ireland Secretary Hilary Benn to act as an interim leader.
This development occurs as insiders report that Sir Keir’s chief of staff, Morgan McSweeney, who is held responsible by Labour MPs for pressuring the Prime Minister to appoint Mandelson—a known associate of Jeffrey Epstein—as US ambassador in 2024, is considering stepping down.
Additionally, Cabinet Secretary Sir Chris Wormald may also be contemplating resignation.
An informed source commented, “Morgan’s departure could serve as a concession to placate the MPs over this debacle. However, the question remains: can Keir continue without him? Ideally, they should both exit together.”
Under the extraordinary caretaker plan, the interim leader would steer Labour beyond the May local elections and then oversee a full-scale party leadership contest in the summer before handing over to the new leader at the party’s annual conference in the autumn.
MPs backing the move say it would ‘bring stability’ to the Government and avoid the ‘bloodbath’ of a leadership contest before May’s elections. It may also appeal to all three of the main leadership contenders – each of whom has reason to want to delay a challenge for the top job.

Labour MPs are lobbying for less contentious candidates to step in for scandal mired Starmer

Keir Starmer has come under heavy fire he admitted he knew Peter Mandelson was still in contact with Jeffery Epstein after he was convicted with child sex offences
For Angela Rayner, it would allow HMRC time to finish its lengthy investigation into her tax affairs and, say backers, ‘lift a shadow’ over her leadership ambitions.
For Manchester Mayor Andy Burnham, it could give him a second chance to claim a Commons seat, without which he cannot succeed Sir Keir.
Mr Burnham, who was blocked from standing in Gorton and Denton by Labour’s ruling National Executive Committee (NEC), is still hoping to secure a constituency in the North West – using the logic that the mood in the party has deteriorated so quickly since he was blocked last month that the NEC would let him stand as Labour’s potential ‘saviour’.
Meanwhile, Health Secretary Wes Streeting would be granted the time needed to shake off his perceived closeness to Mandelson, who has long been regarded as his political mentor.
Last night, one senior Labour MP aware of the plotting conceded that it would require Sir Keir to fall on his sword. But the MP told The Mail on Sunday: ‘Extraordinary times call for extraordinary solutions.
‘We can’t let Starmer limp on until after the May elections – we need a replacement now to stem what could be disastrous losses for Labour. But equally, we can’t have a full-scale election for leader between now and May.’
He said that a respected Cabinet minister without realistic long-term leadership ambitions of their own – ‘such as Hilary Benn or John Healey’ – would be the ideal interim leader.
The MP added: ‘Given the briefing war that’s already broken out between Rayner and Streeting, there wouldn’t be just blood on the walls in a full-on contest – it’d be all over the floor and ceiling, too.
‘And that would only make us lose more seats in May. So yes, the idea is now being discussed actively by Labour MPs.’
It came as:
- Labour MPs warned that Sir Keir would not survive a disastrous result in the Gorton and Denton by-election on February 26.
- Party sources cast doubt on Ms Rayner’s claims to have warned Sir Keir against appointing Mandelson as US ambassador.
- Ed Miliband was tipped to stand for leader on a pledge to do an election deal with the Greens.

Starmer’s chief of staff Morgan McSweeney is close to resigning after claims he pushed for Mandelson to be made ambassador to the US

Less contentious candidates like Defence Secretary John Healey are being proposed by revolting Labour MPs
One Labour MP claimed that despite protestations that Mr Miliband, the Energy Secretary, did not want a second go at the top job, he was waiting ‘like a patient spider in the web’ for the other contenders to fail.
He claimed that Mr Miliband can offer what none of the other main runners could – ‘a deal with the Greens’ to unite the Left vote and prevent Nigel Farage and Reform from gaining power.
There were also claims that, as the two main candidates suspected of having campaigns ready to go, Ms Rayner and Mr Streeting were already plunging the party into ‘civil war’.
Mr Streeting’s backers accused Rayner allies of ‘fantasy stuff’ exaggerations of just how close the Health Secretary was to former Labour grandee Mandelson.
One Streeting ally accused Ms Rayner of ‘virtually salivating’ before she made her crucial intervention in the Commons last week, which forced Sir Keir to back down over the release of documents relating to how Mandelson was appointed US ambassador.
By way of return, Ms Rayner’s camp has celebrated what they see as the collapse of Mr Streeting’s hopes because of his past links to the disgraced New Labour architect. Last night, even one Left-wing MP not aligned to either hopeful joked that Mr Streeting was ‘just a pair of smoking boots’.
However, he also suggested that Ms Rayner ‘isn’t suited to being prime minister’, adding: ‘She doesn’t have what it takes.’
Separately, former deputy PM Ms Rayner came under fire yesterday after reports she had warned Sir Keir not to appoint Mandelson.
One Labour source said: ‘The idea that she was like Cassandra, warning everyone about Mandelson, rings a bit hollow.
‘I know she has the right colour of hair, but she was the one having dinners with him.’
A source close to Ms Rayner said: ‘Not true. [That] didn’t happen’.