Share this @internewscast.com
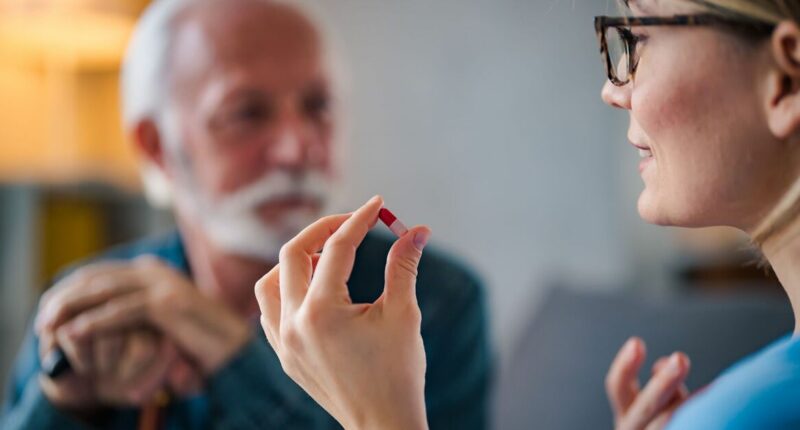
Groundbreaking new Alzheimer’s treatment could give patients four years of better health. Patients who participated in the trial of the drug lecanemab also saw improvements in their cognitive function. Last year, the treatment was licensed for use in the UK after trials demonstrated its ability to slow the progress of the disease.
The results show that, over 18 months, it slowed the progression of Alzheimer’s by 5.7 months. 478 patients then stayed on the drug for four years, which found an average delay of almost 11 months before their disease worsened to the next stage, The Telegraph has revealed. A staggering 69% of patients with low levels of tau – the protein that builds up as Alzheimer’s progresses – saw no decline at all over four years. Over half (56%) of those in the same group also saw major improvements in their cognitive scores.
Patients with mild dementia usually see scores rise by between one and two points each year on the scoring systems used to track Alzheimer’s. However, across the entire group trialling the drug, decline slowed to just 1.75 points over four years.
“The thing I really focus on is the time saved. You will get worse over time, but it will take longer to get there,” Prof Christopher Van Dyck, the director of the Alzheimer’s Research unit at the Yale school of medicine and the study leader, said.
He added that the findings argued the case for starting early treatment of the disease due to it having the best results in people with the lowest pathology.
Experts have since said the new treatments could “meaningfully change the course of the disease”, and not just slow decline.
A separate trail of the similar drug donanemab also showed promising results. Patients were tracked for three years, with the treatment given for just 18 months.
The findings showed that those on the drug had gained between six and 12 months before the disease progressed further, compared to those not on the treatment.
Dr Sheona Scales, the director of research at Alzheimer’s Research UK, told The Telegraph that, while the findings offered renewed hope, research is ongoing.
“This is the first wave of disease-modifying treatments for Alzheimer’s and, while the progress is encouraging, there are still many pieces of the puzzle we don’t yet have,” she said.