Share this @internewscast.com
Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month: Said to be one of the most frequently-diagnosed cancers in the world, colorectal cancer affects people regardless of gender. Early detection can dramatically influence treatment outcomes.
Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month: March is Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month, a disease that is considered to be super aggressive and one that affects younger people, too. Often referred to as bowel cancer, colorectal cancer is a common malignancy that impacts the colon or rectum, which are integral parts of the digestive system. Said to be one of the most frequently-diagnosed cancers in the world, it affects people regardless of gender. Early detection, therefore, can dramatically influence treatment outcomes. In this article, we look at a comprehensive guide on colorectal cancer symptoms, when to seek medical attention, its diagnosis, etc.
Understanding Colorectal Cancer Symptoms
According to Dr Shrikanth R, consultant, medical oncology, HCG NMR Cancer Centre, Hubli, colorectal cancer symptoms can vary depending on its location and stage. While some people may experience no symptoms in the early stages, others may notice subtle signs that indicate a potential problem. Commons symptoms include:
Persistent changes in bowel habits: This may include diarrhoea, constipation, or a change in the consistency of stool that lasts for more than a few days.
Rectal bleeding: Blood in the stool or bleeding from the rectum is another common sign. This bleeding may be bright red or dark in colour and may occur during bowel movements or spontaneously.
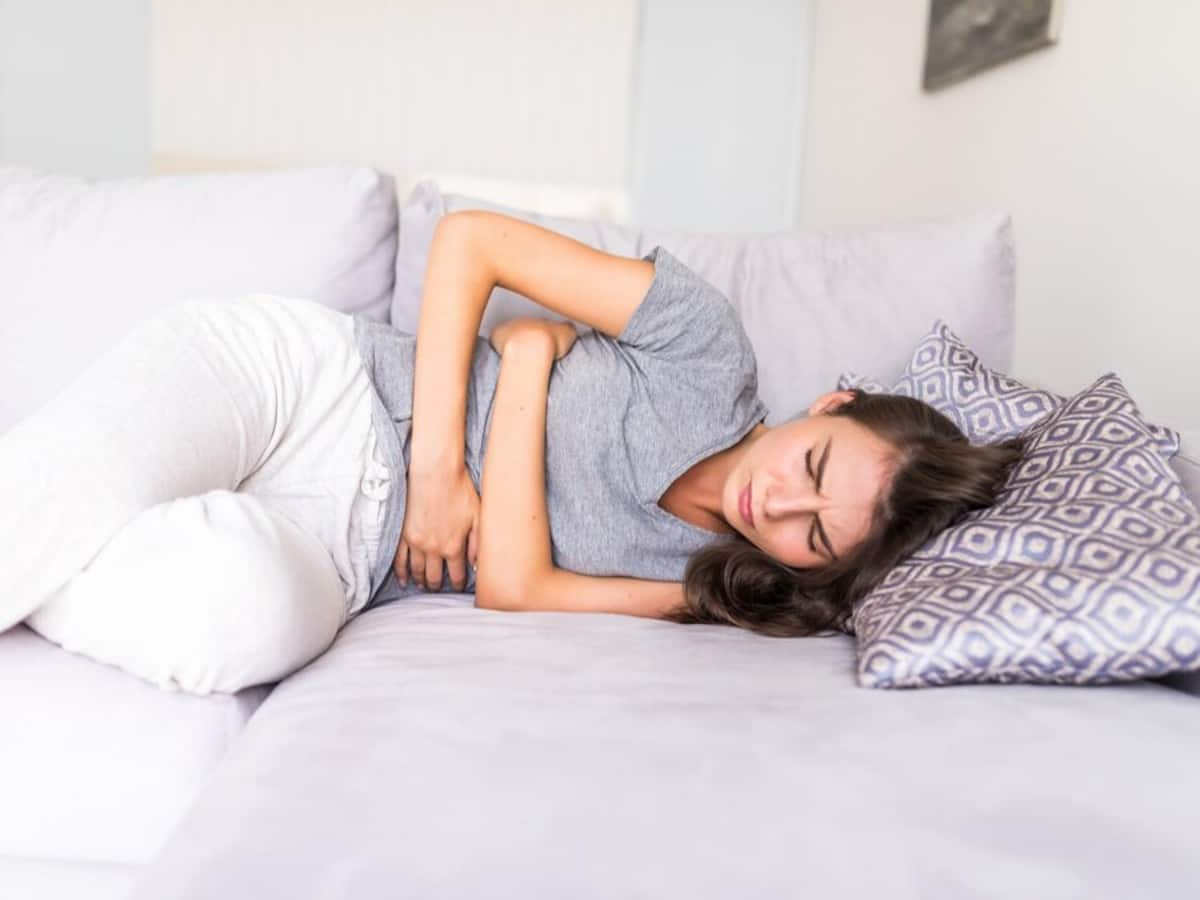
Abdominal discomfort: Individuals with colorectal cancer may experience abdominal pain, cramping, or discomfort that does not go away. This pain may be localised or diffuse and may worsen over time.
Unexplained weight loss: Unintentional weight loss without changes in diet or exercise habits can be a symptom, particularly in advanced stages.
Fatigue and weakness: Chronic fatigue and weakness can occur because of anaemia caused by rectal bleeding or reduced nutrient absorption due to colorectal cancer.
Feeling of incomplete evacuation: Some individuals with colorectal cancer may experience a sensation of incomplete evacuation after bowel movements, even if the bowel is empty.
Changes in bowel diameter: Narrowing of the stool or a feeling of incomplete bowel emptying due to obstruction by a tumor may indicate advanced colorectal cancer.
When To Seek Medical Attention?
“Consult a healthcare professional if you experience any of the symptoms, particularly if they persist for more than a few weeks or worsen over time. Early detection and treatment significantly improve the prognosis for colorectal cancer, so it is crucial not to ignore potential warning signs,” the doctor said.

Diagnostic Tests for Colorectal Cancer
If colorectal cancer is suspected, your healthcare provider may recommend various diagnostic tests:
Colonoscopy: A procedure in which a flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the rectum to examine the colon and rectum for abnormalities.
Fecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT): A test that detects hidden blood in the stool, which may indicate the presence of colorectal cancer.
Imaging tests: Imaging tests like CT scans, MRI scans, or ultrasound may be used to visualise the colon and rectum to identify abnormalities.
Treatment Strategies
Dr Shrikanth said treatment strategies are determined based on the cancer’s stage and its extent.
Surgery is often the primary treatment, aiming to remove the cancerous growth and possibly nearby lymph nodes.
Chemotherapy is another treatment that utilises drugs to kill or inhibit cancer cells, administered before (neoadjuvant) or after (adjuvant) surgery, or as the main therapy for advanced cancer.
Radiation therapy employs high-energy beams to eradicate cancer cells, used pre- or post-surgery, or in conjunction with chemotherapy.
Targeted therapy targets specific cancer cell abnormalities.
Immunotherapy treatment aids the immune system in identifying and attacking cancer cells, particularly effective for advanced cases with specific genetic traits.