Share this @internewscast.com
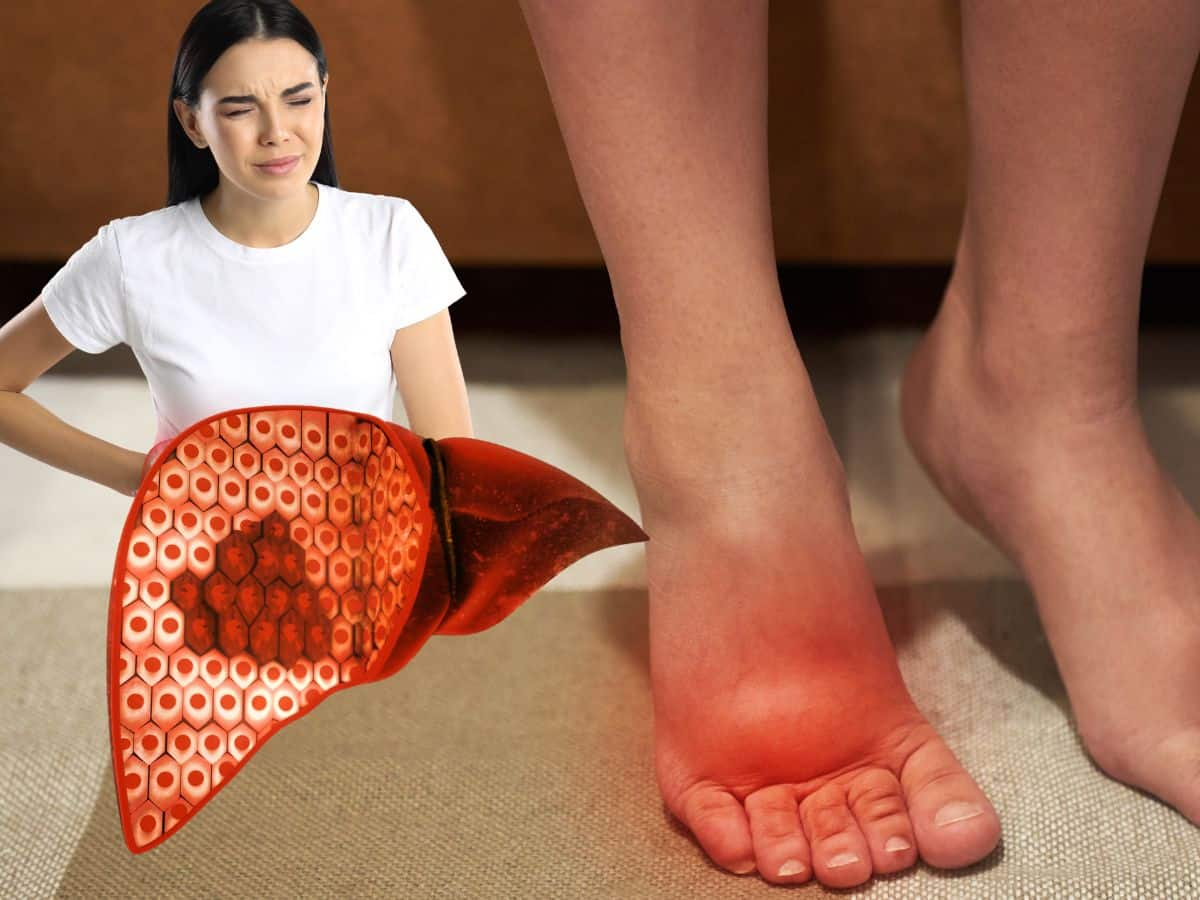

Are you suffering from fatty liver disease? Look out for these unusual swelling in your body parts that could indicate liver damage.
Fatty Liver Disease Symptoms: Your liver is an essential organ performing essential duties to retain stellar health. It detoxifies, produces vital proteins, and aids the digestion process, thus helping to prevent the pile-up of dangerous compounds that can cause health complications. However, this essential organ is vulnerable to a lot of health problems, including liver damage, and fatty liver disease. In this article, we delve into how fatty liver disease affects the body, and what signs and symptoms the body may show up after developing this condition.
Fatty Liver Disease: What You Need To Know
Fatty liver disease is a condition that affects many individuals worldwide. It is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver cells, leading to potential liver damage. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of severe liver damage is crucial in managing this condition effectively. But before we get into how to recognise the condition, let’s take a look at what the disease actually looks like. An overload of fat clogging the liver can result in fatty liver disease Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, occurs when excess fat builds up in the liver. This can be caused by various factors such as obesity, high cholesterol, or excessive alcohol consumption. While a small amount of fat in the liver is normal, excessive fat can lead to inflammation and liver damage.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease
A fatty liver, marked by the build-up of fat in liver cells, might signify inflammation in several parts of your body. Neglecting liver damage brought about by this condition can dangerously impact your health and well-being. To avert serious complications that the condition can trigger if proper care is not taken on time, you need to have an idea about its subtle signs and symptoms. In this piece, we tell you the unusual swellings that can indicate liver damage.
Puffy Eyes
It’s rather unsettling when your eyes start yellowing, a condition known as jaundice, and it could be the initial sign of substantial liver dysfunction. This happens because bilirubin is over-accumulated in the body when the liver can’t process it effectively, causing the eyes and skin to get a yellowish tint.
Abdominal Swelling
If your abdomen swells up suddenly or severely, it could be ascites, a symptom of advanced liver disease – a situation that calls for immediate medical help. Ascites lead to discomfort and distension in the abdomen due to fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity, pointing to significant liver damage.
Swollen Legs
Next up is oedema, a condition that manifests as swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet due to fluid retention, commonly found in severe liver disease cases. It can cause discomfort, pain, and decreased mobility a clear call for immediate medical review.
Unusually Swollen Hands
Notice swelling in your hands and fingers? That’s another potential sign of severe liver damage. People in the advanced stages of liver disease may experience fluid retention that causes the hands to swell, affecting dexterity and hand function. Thus, it underscores the urgency to tackle any liver health problems quickly.
Heaviness on the Chest Due to Inflammation
Suppose you feel an unusual tightness or swelling in your chest this could be another indication of substantial liver damage, often making breathing difficult. It’s crucial to get immediate medical help in such situations to evaluate and control any impending complications.
Face Swelling
Facial swelling, primarily around the eyes and cheeks, might be signalling serious liver damage too. Known as facial oedema, this change can impact self-esteem as well as appearance. Thus, addressing the root cause, that is the liver issue, becomes essential to manage this symptom and stop further complications.
Swollen Feet
Lastly, if you observe swelling or tightness in your feet, making extended standing or walking uncomfortable, it might be another red flag for liver damage. Keeping a check on such symptoms and seeking medical guidance will aid in pinpointing any liver-related issues.
Fatty Liver Disease: Importance of Understanding The Symptoms of Liver Inflammation
Recognising the above-mentioned top 7 unusual signs of fatty liver disease is important. These swellings in various body parts could indicate the onset of this condition. Any experience of these symptoms necessitates a consultation with a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and apt treatment. Taking action on liver health early helps avert future complications, boosting overall well-being.