Share this @internewscast.com
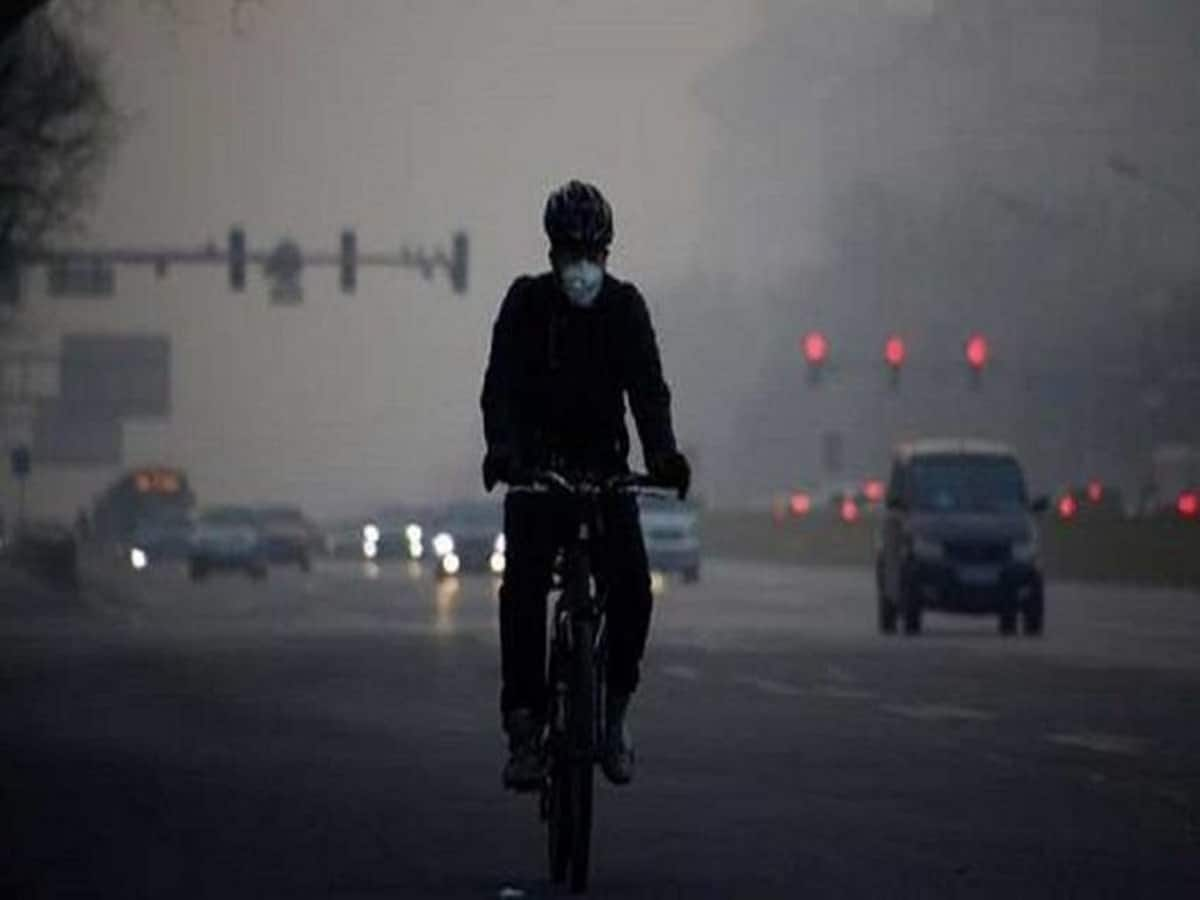

The presence of fog and smog, both by-products of air pollution, considerably affect our health. Read on to know the implications and solutions.
Two prevailing atmospheric phenomena, fog and smog, have a weighty influence on human health. Both are birthed from air pollutants yet they are distinctive in their makeup and environmental effects. Herein, we delve into the health ramifications of fog and smog and mull over effective ways of alleviating their detrimental impacts.
The thick moisture-laden fog not only intensifies respiratory problems but also accelerates the spread of airborne diseases. On the other hand, smog, a deadly mix of fog and smoke, is infamous for triggering respiratory problems and heart diseases, heightening the odds of heart troubles and lung cancer. In order to keep these health risks at bay, it’s essential to cut down emissions and adopt individual safety measures like mask-wearing and ensuring good ventilation. It’s crucial that we comprehend this.
Fog Explained
Imagine a cloud hanging low; that’s what fog is. It emerges when moist air brushes up against a cooler surface. Composed of minuscule water droplets or ice crystals floating in the air, fog significantly shrinks visibility to less than a kilometer, especially common near the coast and in chillier parts of the year.
Health effects of fog
Fog, with its high humidity, can adversely affect our respiratory system leading to coughing fits, labored breathing, and wheezing. If you have respiratory ailments like asthma or COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) you may your conditions worsening in foggy weather.
Interestingly, fog could also increase airborne diseases as bacteria and viruses find the moist conditions perfect for their growth. Therefore, it’s wise to wear masks and follow good hygiene practices during foggy times to reduce contracting illnesses.
Decoding Smog
Smog is essentially a cocktail of smoke and fog, a brand of air pollution mostly triggered by vehicle emissions, industrial activities, and fossil fuel combustion. Smog is usually an unwelcome guest in urban spaces laden with air pollution.
Health effects of smog
Smog is notorious for causing severe health issues, particularly targeting our respiratory and cardiovascular systems. Pollutants like nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and airborne particles within smog can inflame our lungs. Be aware – habitual exposure to smog could exacerbate respiratory issues like asthma and bronchitis.
Smog can also intrude on our bodies more systemically. The tiny particles can sneak into our bloodstream and meddle with our cardiovascular system, thereby escalating risks of heart problems, strokes, and other heart-related diseases. Long-term smog exposure could diminish lung function, hasten death, and spike lung cancer risk.
A few tips for you
To alleviate the health impacts of fog and smog, certain strategies can be implemented. We can start by slashing the emissions responsible for smog – this can happen through cleaner fuel utilization, encouraging eco-friendly public transportation usage, and enforcing rigorous emission norms for vehicles and industries.
Moreover, personal steps like wearing masks with fine particle filters, restricting outdoor activity when the air quality plummets, and maintaining well-ventilated indoor spaces with air purifiers can protect us during dense fog and smog circumstances.
The last word
Fog and smog pack a punch when it comes to impacting health, particularly respiratory and cardiovascular systems. Understanding these phenomena is key to forming effective strategies to soften their blow on health. By curtailing emissions and upgrading personal precautionary measures, we can contribute to enhancing air quality and shield our health.