Share this @internewscast.com
Meat is a staple in many diets worldwide, prized for its protein, iron, and flavor. However, overindulging in meat—especially processed or red varieties—can trigger serious health consequences. From kidney strain to heightened heart disease risk, this article explores the science-backed effects of excessive meat consumption and offers actionable advice for maintaining balance.
How Excessive Meat Consumption Increases Kidney Stone Risk
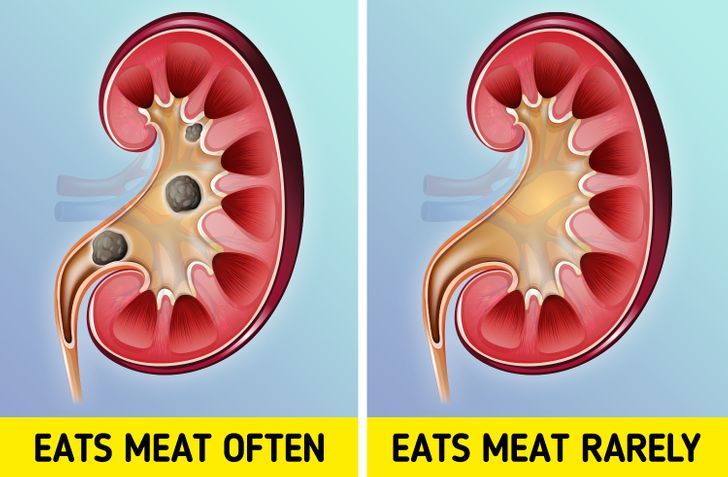
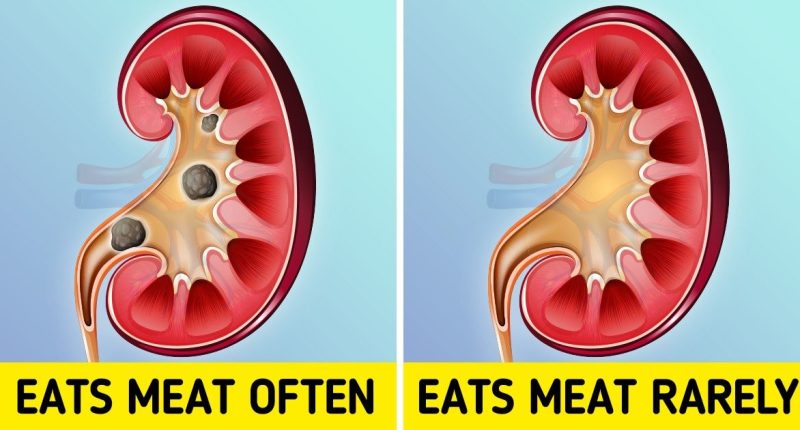
High meat intake, particularly red and processed meats, elevates uric acid and calcium levels in the body. These compounds crystallize in the kidneys, forming painful stones. A study by the National Kidney Foundation found that diets rich in animal protein increase urinary calcium excretion by 50%, directly raising kidney stone risk.
Key factors:
- Purine overload: Organ meats and certain fish (e.g., sardines) are high in purines, which metabolize into uric acid.
- Low citrate levels: Meat-heavy diets reduce citrate, a compound that prevents stone formation.
To mitigate risk, balance protein sources with plant-based options like lentils and tofu, and stay hydrated.
The Link Between High Meat Intake and Dehydration
A protein-dense diet forces your kidneys to work harder to flush out nitrogen waste, a byproduct of protein breakdown. This process increases urine output, potentially leading to dehydration. According to the Mayo Clinic, symptoms like dry mouth, fatigue, and dizziness may signal fluid imbalance.
Why it matters:
- Electrolyte imbalance: Excessive urination depletes sodium and potassium, crucial for muscle and nerve function.
- Athletes beware: Those on high-protein diets for muscle gain are especially prone to dehydration.
Pair meat meals with water-rich vegetables (e.g., cucumbers, celery) and aim for 8–10 glasses of water daily.
Can Eating Too Much Meat Cause Constipation?
Meat lacks dietary fiber, a nutrient essential for healthy digestion. Over time, a low-fiber diet slows gut motility, leading to constipation. The CDC recommends 25–30 grams of fiber daily, yet meat-heavy eaters often fall short.
Digestive fixes:
- Add fiber gradually: Integrate whole grains, fruits, and legumes to avoid bloating.
- Limit processed meats: Bacon and sausages are high in salt, which can worsen constipation by dehydrating stools.
Meat Consumption and Headaches: The Hidden Connection

Processed meats contain nitrates and nitrites, preservatives linked to migraines. A 2021 study in Nutrients found that dietary nitrates trigger headaches by dilating blood vessels. Additionally, dehydration from high protein intake exacerbates the issue.
Common culprits:
- Deli meats: Ham, salami, and hot dogs are nitrate-rich.
- Tyramine-containing meats: Aged or fermented meats (e.g., pepperoni) contain tyramine, a compound linked to migraines.
Opt for fresh, unprocessed meats and pair them with magnesium-rich foods like spinach to reduce headache frequency.
Excessive Meat Intake and Heart Disease: What You Need to Know

Red and processed meats are loaded with saturated fats and cholesterol, which contribute to arterial plaque buildup. The American Heart Association warns that daily red meat consumption raises cardiovascular disease risk by 22%.
Alarming stats:
- Saturated fat overload: A 6-oz steak contains 12g of saturated fat—60% of the daily limit.
- TMAO production: Gut bacteria convert carnitine (abundant in red meat) into TMAO, a compound linked to heart attacks.
Swap red meat for fatty fish like salmon, rich in heart-healthy omega-3s, twice weekly.
Does a Meat-Heavy Diet Weaken Your Immune System?

High meat consumption may impair immune function by promoting inflammation and gut dysbiosis. Processed meats’ advanced glycation end products (AGEs) trigger chronic inflammation, while a lack of plant-based antioxidants leaves the body vulnerable to pathogens.
Research highlights:
- A Harvard study found that diets high in red meat alter gut microbiota, reducing beneficial bacteria.
- Zinc imbalance: While meat provides zinc, excessive intake suppresses copper absorption, weakening immune response.
Incorporate probiotic-rich foods (e.g., yogurt) and colorful vegetables to bolster immunity.
Balancing Your Diet for Long-Term Health
Moderation is key. The WHO recommends limiting red meat to 1–2 servings weekly and avoiding processed meats. Try these tips:
- Meatless Mondays: Explore plant-based proteins like chickpeas or quinoa.
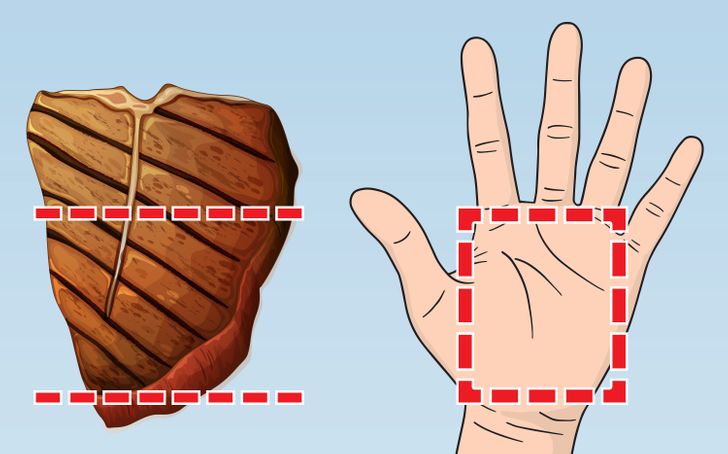
- Portion control: Stick to 3–4 oz servings (about the size of a deck of cards).
- Choose lean cuts: Opt for chicken breast or turkey over fatty ribs.
Conclusion
While meat offers vital nutrients, overconsumption strains kidneys, dehydrates the body, and heightens chronic disease risk. By diversifying protein sources and prioritizing whole foods, you can enjoy meat safely while safeguarding your health. Always consult a nutritionist to tailor dietary choices to your needs.
Preview photo credit depositphotos.com