Share this @internewscast.com

TANZANIA – In a bid to quell a devastating conflict that has persisted for nearly 1,000 days, Sudan’s Prime Minister has unveiled a comprehensive peace initiative aimed at resolving the war with a rival paramilitary faction. Despite this, the United States has urged both parties to heed the Trump administration’s call for an immediate humanitarian ceasefire.
Kamil Idris, the leader of Sudan’s transitional civilian government, presented his plan to the United Nations Security Council. The proposal includes a ceasefire to be overseen by the United Nations, African Union, and Arab League. It also demands the withdrawal of paramilitary forces from occupied territories, their relocation to monitored camps, and subsequent disarmament.
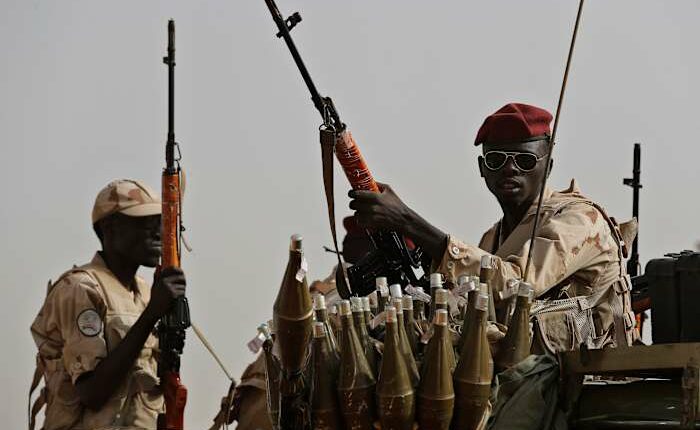
This conflict erupted into chaos in April 2023 due to a power struggle between the military and the Rapid Support Forces (RSF), a formidable paramilitary group. The ensuing violence has resulted in mass atrocities, including widespread killings and rapes, often driven by ethnic motivations. The United Nations and international human rights organizations have classified these acts as war crimes and crimes against humanity.
The prime minister’s initiative, however, faces skepticism. It is improbable that the RSF will embrace a plan that effectively hands victory to government forces while stripping the paramilitary group of its military influence.
Addressing the U.N. Security Council, Idris emphasized that the government’s proposal was independently crafted, in what seemed a veiled response to the truce advocated by the U.S. and the so-called Quad—Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and the United Arab Emirates. Idris asserted that the proposal is “homemade — not imposed on us.”
Earlier in November, the Rapid Support Forces had agreed to a humanitarian truce. At that juncture, a Sudanese military official informed The Associated Press that while the army was open to the Quad’s proposal, it would only consent to a ceasefire if the RSF withdrew entirely from civilian areas and surrendered their arms—conditions central to Idris’s plan presented on Monday.
Idris said unless the paramilitary forces were confined to camps, a truce had “no chance for success.” He challenged the 15 members of the Security Council to back his proposal.
“This initiative can mark the moment when Sudan steps back from the edge and the international community — You! You! — stood on the right side of history,” the Sudanese prime minister said. He said the council should “be remembered not as a witness to collapse, but as a partner in recovery.”
U.S. deputy ambassador Jeffrey Bartos, who spoke to the council before Idris, said the Trump administration has offered a humanitarian truce as a way forward and “We urge both belligerents to accept this plan without preconditions immediately.”
Bartos said the Trump administration strongly condemns the horrific violence across Darfur and the Kordofan region — and the atrocities committed by both the Sudanese Armed Forces and the Rapid Support Forces, who must be held accountable.
UAE Ambassador Mohamed Abushahab, a member of the Quad, said there is an immediate opportunity to implement the humanitarian truce and get aid to Sudanese civilians in desperate need.
“Lessons of history and present realities make it clear that unilateral efforts by either of the warring parties are not sustainable and will only prolong the war,” he warned.
Abushahab said a humanitarian truce must be followed by a permanent ceasefire “and a pathway towards civilian rule independent of the warring parties.”
U.N. Assistant Secretary-General for political affairs Khaled Khiari reflected escalating council concerns about the Sudan war, which has been fueled by the continuing supply of increasingly sophisticated weapons.
He criticized unnamed countries that refuse to stop supplying weapons, and both government and paramilitary forces for remaining unwilling to compromise or de-escalate.
“While they were able to stop fighting to preserve oil revenues, they have so far failed to do the same to protect their population,” Khiari said. “The backers of both sides must use their influence to help stop the slaughter, not to cause further devastation.”
The devastating war in Sudan has killed more than 40,000 people according to U.N. figures, but aid groups say the true number could be many times higher. The conflict has created the world’s largest humanitarian crisis, with over 14 million people displaced, disease outbreaks and famine spreading in parts of the country.
Copyright 2025 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without permission.