Share this @internewscast.com
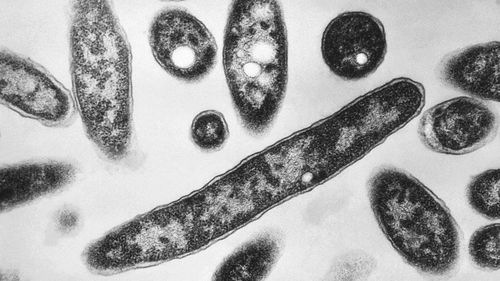
In New York City, fifty-eight individuals have been confirmed to have Legionnaires’ disease, a severe bacterial infection of the lungs, resulting in two fatalities, as reported by the city health department.
The bacteria, Legionella, is suspected to be spread by cooling towers on buildings in Central Harlem.
A cooling tower is a rooftop device that releases mist into the air as it cools a large building.

Legionnaires’ disease causes flu-like symptoms, including cough, fever, headaches, muscles aches and shortness of breath.
It’s treatable with antibiotics, but if left untreated, it can cause shock and multi-organ failure, according to the World Health Organisation.
According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, approximately 10% of those who contract Legionnaires’ disease succumb to complications related to the illness. It poses a greater threat to older adults and individuals with compromised immune systems.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration estimates about 6,000 cases of Legionnaires’ disease occur annually in the United States. However, the number of reported cases might be an understatement since distinguishing Legionnaires’ disease from other pneumonia types can be challenging.