Share this @internewscast.com
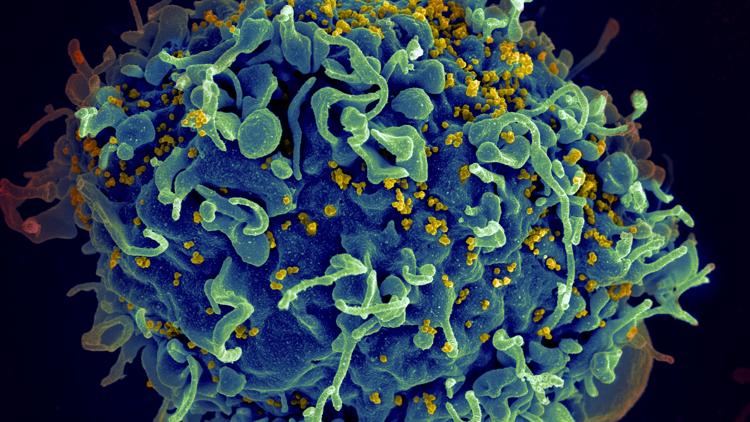
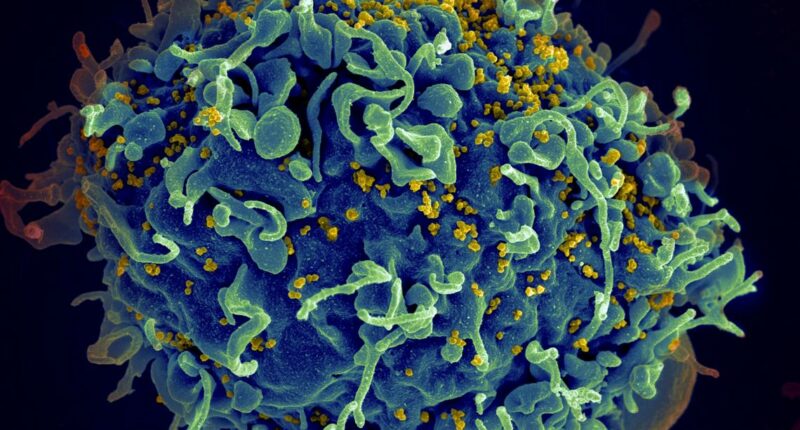
The U.S. had committed $4 billion for the worldwide HIV initiative aimed at 2025, but this funding vanished almost instantly when President Donald Trump assumed office in January.
WASHINGTON — Decades of U.S.-led financial support for AIDS initiatives have decreased the death toll from the disease to its lowest in over thirty years, and have delivered essential medicines to some of the most at-risk global populations.
However, within the last six months, U.S. funding withdrawal has triggered a “systemic shock,” as stated by U.N. officials. They cautioned that if this financial gap isn’t filled, it might result in over 4 million AIDS-related deaths and an additional 6 million HIV infections by 2029.
“The current wave of funding losses has already destabilized supply chains, led to the closure of health facilities, left thousands of health clinics without staff, set back prevention programs, disrupted HIV testing efforts and forced many community organizations to reduce or halt their HIV activities,” UNAIDS said in a report released Thursday.
UNAIDS also said that it feared other major donors might also scale back their support, reversing decades of progress against AIDS worldwide — and that the strong multilateral cooperation is in jeopardy because of wars, geopolitical shifts and climate change.
The $4 billion that the United States pledged for the global HIV response for 2025 disappeared virtually overnight in January when U.S. President Donald Trump ordered that all foreign aid be suspended and later moved to shutter the U.S. AID agency.
Andrew Hill, an HIV expert at the University of Liverpool who is not connected to the United Nations, said that while Trump is entitled to spend U.S. money as he sees fit, “any responsible government would have given advance warning so countries could plan,” instead of stranding patients in Africa when clinics were closed overnight.
The U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief, or PEPFAR, was launched in 2003 by U.S. President George W. Bush, the biggest-ever commitment by any country focused on a single disease.
UNAIDS called the program a “lifeline” for countries with high HIV rates, and said that it supported testing for 84.1 million people, treatment for 20.6 million, among other initiatives. According to data from Nigeria, PEPFAR also funded 99.9% of the country’s budget for medicines taken to prevent HIV.
In 2024, there were about 630,000 AIDS-related deaths worldwide, per a UNAIDS estimate — the figure has remained about the same since 2022 after peaking at about 2 million deaths in 2004.
Even before the U.S. funding cuts, progress against curbing HIV was uneven. UNAIDS said that half of all new infections are in sub-Saharan Africa.
Tom Ellman, of the charity Doctors Without Borders, said that while some poorer countries were now moving to fund more of their own HIV programs, it would be impossible to fill the gap left by the U.S.
“There’s nothing we can do that will protect these countries from the sudden, vicious withdrawal of support from the U.S.,” said Ellman, director of Doctors Without Borders’ South Africa Medical Unit.
Experts also fear another loss: data. The U.S. paid for most HIV surveillance in African countries, including hospital, patient and electronic records, all of which has now abruptly ceased, according to Dr. Chris Beyrer, director of the Global Health Institute at Duke University.
“Without reliable data about how HIV is spreading, it will be incredibly hard to stop it,” he said.
The uncertainty comes as a twice-yearly injectable could end HIV, as studies published last year showed that the drug from pharmaceutical maker Gilead was 100% effective in preventing the virus.
At a launch event Thursday, South Africa’s health minister Aaron Motsoaledi said the country would “move mountains and rivers to make sure every adolescent girl who needs it will get it,” saying that the continent’s past dependence upon US aid was “scary.”
Last month, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved the drug, called Yeztugo, a move that should have been a “threshold moment” for stopping the AIDS epidemic, said Peter Maybarduk of the advocacy group Public Citizen.
But activists like Maybarduk said Gilead’s pricing will put it out of reach of many countries that need it. Gilead has agreed to sell generic versions of the drug in 120 poor countries with high HIV rates but has excluded nearly all of Latin America, where rates are far lower but increasing.
“We could be ending AIDS,” Maybarduk said. “Instead, the U.S. is abandoning the fight.”
Copyright 2025 Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed.