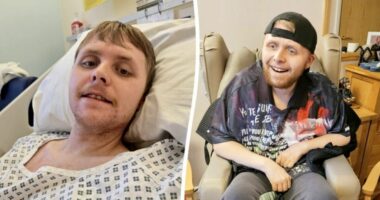
Share this @internewscast.com
Close to all new COVID-19 cases in the United States are now being caused by the JN.1 variant, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says, with an estimated 93.1% of infections now blamed on the highly mutated strain.
The CDC’s latest biweekly estimate of the variant’s spread was published Friday. It comes as key trends reflecting COVID-19’s spread are now showing signs of slowing, following a peak over the winter holidays.
“Several key indicators are showing decreasing levels of activity nationally,” the agency said Friday in its weekly respiratory viruses report.
Only the South has seen trends of the virus rise in wastewater over recent weeks, according to the CDC’s tally through Feb. 1.
Most parts of the country are also seeing steep slowdowns in COVID-19 cases diagnosed in emergency rooms, except in the South where trends now appear to have roughly plateaued in some states.
The agency also published new data Thursday from its pharmacy testing program that suggests this season’s updated COVID-19 vaccines had 49% effectiveness against symptomatic JN.1 infection, among people between two to four months since they got their shot.
“New data from CDC show that the updated COVID-19 vaccines were effective against COVID-19 during September 2023 – January 2024, including against variants from the XBB lineage, which is included in the updated vaccine, and JN.1, a new variant that has become dominant in recent weeks,” the CDC said in a post on Thursday.
CDC officials have said that other data from ongoing studies using medical records also offered “early signals” that JN.1’s severity was indeed not worse than previous strains. That is a step beyond the agency’s previous statements simply that there was “no evidence” the strain was causing more severe disease.
The CDC’s new variant estimates mark the culmination of a swift rise for JN.1, which had still made up less than half of infections in the agency’s estimates through late December.
Some of the earliest samples of the strain in the global virus database GISAID date back to August, when cases of JN.1 – a descendant of an earlier worrying variant called BA.2.86 – showed up in Iceland and Luxembourg.
By the end of September, at least 11 cases had been sequenced in the U.S., prompting renewed concern that BA.2.86 had picked up changes that were accelerating its spread around the world.
The World Health Organization stepped up its classification of JN.1 to a standalone “variant of interest” in mid-December, citing the variant’s rapid ascent. Health authorities in the U.S. have declined to do the same, continuing to lump the strain in with its BA.2.86 parent.