Share this @internewscast.com

In a groundbreaking move, the Tallgrass Trailblazer Pipeline began operations in September, marking a significant step forward in the realm of carbon capture technologies. This multi-state initiative aims to mitigate emissions from Midwestern ethanol plants by transporting carbon dioxide to a storage site deep beneath the earth in Wyoming. This achievement comes after years of obstacles faced by similar ventures, including public backlash, legal challenges, and legislative hurdles.
Unlike other high-profile projects that have encountered fierce opposition and hefty price tags, the Tallgrass Pipeline is earning accolades for its unique approach. The secret to its success lies in a strategy that emphasizes community engagement and financial backing, setting it apart from other initiatives in this space.
Jane Kleeb, a prominent figure in environmental advocacy through her organization Bold Nebraska, commended Tallgrass for its respectful dealings with local communities. “I wish all energy companies would treat communities with a lot more respect like Tallgrass did,” she remarked, having been a staunch opponent of other carbon capture and oil pipeline projects.
Carbon capture pipelines
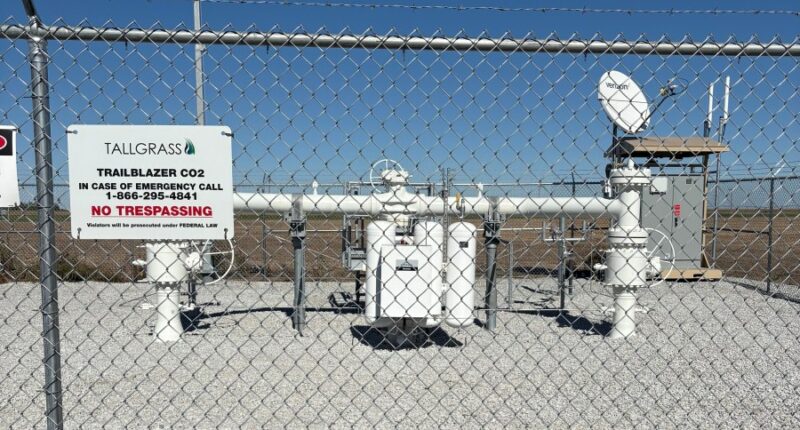
This ambitious pipeline now facilitates the transfer of emissions from 11 ethanol plants in Nebraska and one in Iowa, channeling the captured carbon dioxide to a designated site in southeastern Wyoming. There, the greenhouse gas is securely sequestered 9,000 feet underground, preventing its release into the atmosphere.
The process of converting corn into ethanol fuel inherently produces carbon dioxide. By capturing this gas before it escapes, the ethanol plants can significantly reduce their carbon intensity scores. This reduction not only enhances the environmental profile of ethanol but also positions it as a viable feedstock for sustainable aviation fuel — a burgeoning market that some experts anticipate could grow to a staggering 50 billion gallons annually. As the demand for traditional motor vehicle fuel is expected to decline with the rise of electric vehicles, the ethanol industry is keenly eyeing jet fuel as a crucial avenue for future growth.
The federal government has been a strong supporter of carbon capture endeavors, offering substantial tax incentives to pipeline operators. This initiative receives endorsement from both the Biden and Trump administrations, reflecting a bipartisan consensus on the importance of reducing greenhouse gas emissions through innovative technological solutions.
“If an ethanol plant captures the carbon, it lowers their carbon index and they become a low-carbon fuel, and there’s a premium for that,” said Tom Buis, CEO of the American Carbon Alliance, a trade group. “And they can also produce sustainable aviation fuel out of it. Sustainable aviation fuel is a huge, gigantic market just waiting for someone to step forward and take it.”
Routing a pipeline isn’t easy
At least three other companies have proposed carbon capture pipelines in the Midwest, but aside from Tallgrass, only Iowa-based Summit Carbon Solutions is persisting — and it hasn’t been easy.
Summit has proposed a multibillion-dollar, five-state pipeline network encompassing dozens of ethanol plants, thousands of miles and underground storage in North Dakota.
Despite strong support from agricultural groups and the ethanol industry, Summit has dealt with persistent opponents who don’t want their land taken for the pipeline and fear a hazardous pipe rupture. Landowners sued to block the pipeline and sought help from legislators. South Dakota’s legislature banned the use of eminent domain for such lines.
In response Summit has asked Iowa regulators to amend its permit so the company retains an option for a route that would avoid South Dakota.
“Our focus remains on supporting as many ethanol partners as possible and building a strong foundation that helps farmers, ethanol plants, and rural communities access the markets they’ll depend on for decades to come,” Summit said in a statement.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency oversees a rigorous process for underground carbon dioxide injection, involving permits for construction and injection and regulations to protect underground sources of drinking water, Carbon Capture Coalition Executive Director Jessie Stolark said. Typically, porous rock formations similar to a sponge will store or trap the carbon dioxide more than a mile underground, she said.
How did Tallgrass do it?
Tallgrass had one big advantage at the starting point — it converted an existing natural gas line. The natural gas was put on a different pipeline as Trailblazer was retrofitted. The company built branches off the 400-mile mainline to connect to ethanol plants.
But Tallgrass also took pains to engage with communities along its route.
The company worked with people to get its project done “instead of trying to push it down our throat,” said Lee Hogan, chairman of the Adams County commission in Nebraska, whose home is a half-mile from the pipeline.
It helped that Tallgrass worked with Bold Nebraska, a citizens group, to create a community investment fund that will make annual payments to organizations related to early childhood development, Medicaid-eligible senior care and food pantries.
Tallgrass will make an initial $500,000 contribution followed by annual payments based on 10 cents per metric ton of carbon dioxide sent through the pipeline. The Nebraska Community Foundation, which will manage the fund, expects more than $7 million will be given out through 2035 across 31 counties in four states.
It’s a unique arrangement, and a possible template for future projects, said Nebraska Community Foundation leader Jeff Yost.
“I’m just really impressed that folks that could have just approached this purely as opponents have come together to find a really productive middle ground,” Yost said.
Tallgrass spokesman Steven Davidson said the investment fund is just one piece of the company’s agreement with Bold, which he said emphasizes being cooperative and transparent, such as when surveying land and valuing easements.
Lessons from Tallgrass
While lauding Tallgrass’ cooperative approach, Jack Andreasen Cavanaugh, who studies energy policy at Columbia University, said it may be hard to replicate the experience since few if any natural gas pipelines will be available for retrofitting, given increases in supply and demand for natural gas domestically and abroad. Tallgrass’ line crosses his family’s land in Nebraska.
Still, companies can do better to engage and negotiate with communities, and that includes spending money, he said.
Kyle Quackenbush, a Tallgrass vice president, said his advice to other pipeline companies is to listen.
“I think the biggest advice we would have for people is to take those concerns seriously,” he said, “and figure out what it takes to be able to help people get comfortable and understand that this infrastructure is a benefit for their community and not something that they need to be afraid of.”