Share this @internewscast.com

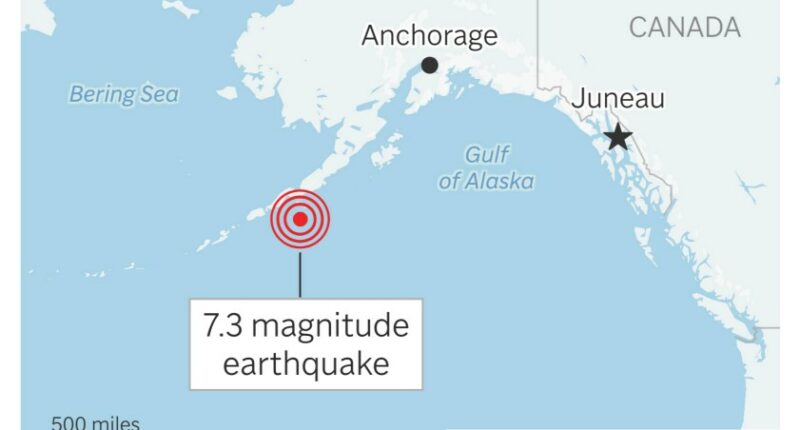
An earthquake with a magnitude of 7.3 occurred off the Aleutian Islands in Alaska on Wednesday. This region has experienced several strong earthquakes over the past five years, including one almost exactly two years prior that affected local communities.
Officials on Thursday reported no reports of injuries or significant damage from the recent quake. It led to a tsunami warning for about an hour, which was later downgraded. This prompted action along a 700-mile (1,127-km) section of Alaska’s southern coastline, urging residents to seek higher ground. The highest recorded wave was about 3.9 inches (10 centimeters) at Sand Point, a location 55 miles (88 kilometers) from the quake’s center, occurring during low tide, according to Kara Sterling, a scientist at the National Tsunami Warning Center.
Earthquake sparked tsunami warnings
The earthquake struck at 12:37 p.m. local time, prompting the center’s tsunami warning.
Residents in the affected areas can receive warnings through various methods, such as sirens, weather radio, public radio broadcasts, social media updates, and cellphone alerts. In some regions, officials may even go door to door to spread the warning, as mentioned by Jeremy Zidek, a state emergency management spokesperson.
Public safety departments in King Cove and Unalaska sent alerts urging those in coastal areas or those that could see inundation to seek higher ground.
The warning issued by the center was downgraded to an advisory before being canceled around 2:45 p.m.
Alaska is one of world’s most seismically active regions
Alaska is the most earthquake-prone state in the U.S. and one of the most seismically active regions in the world, according to the U.S. Geological Survey. The state experiences a magnitude 7 earthquake almost annually, and the second-largest earthquake ever recorded was centered about 75 miles (120 kilometers) east of Anchorage, the agency said. That 1964 magnitude 9.2 earthquake — and the tsunami it triggered — killed about 130 people.
The Aleutian arc is no stranger to earthquakes, but the activity in the region where Wednesday’s earthquake struck has gotten scientists’ attention. The area, within a few hundred miles of the earthquake, has “lit up” since 2020, with Wednesday’s earthquake marking the fifth exceeding magnitude 7.0 since 2020, said state seismologist Michael West.
“I would not call this an isolated earthquake. It appears to be part of a larger sequence spanning the last several years,” he said. But West added: “There’s no reason to be alarmist about this.”
People should continue to heed warnings, officials say
Some communities have buildings designated on higher ground as meetup points during tsunami warnings, such as a school, while others might simply urge residents to retreat up a hillside, Zidek said.
“That area of Alaska, most areas of Alaska, it gets steep real quick,” he said.
Sometimes, the only warning one might have is the shaking ground, Zidek said. “If it shakes violently for 20 seconds or more, that is your warning sign, and you should head to higher ground if you’re in a coastal area,” he said.
Zidek and West said people should continue to heed warnings. West said he worries about a “burnout effect” among residents in the region, some of whom have evacuated numerous times since 2018 in response to larger earthquakes that have not caused significant damage.
West said he is reminded of a magnitude 8.6 earthquake in 1946 — west of the location of Wednesday’s quake — that generated a deadly tsunami and led to the creation of a U.S. tsunami warning system. The death toll included more than 150 people in Hawaii, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
“This area is capable of trans-Pacific tsunamis, and I feel like maybe the best way to stay vigilant … is maybe to look into our deeper history beyond just the last five years,” he said.