Share this @internewscast.com
Earlier this year, Argentine President Javier Milei unveiled and declassified a significant collection of documents related to some of the most notorious Nazi war criminals. This extensive archive, exceeding 1,850 documents, sheds light on the South American nation’s attempts to locate and authenticate the whereabouts of numerous Nazis who sought refuge in Argentina following World War II.
This initiative was driven by the Senate Judiciary Committee, spearheaded by Chairman Chuck Grassley, a Republican from Iowa. His contributions were acknowledged by the Simon Wiesenthal Center for persuading President Milei to make these documents public.
Most of these documents pertain to investigations conducted from the late 1950s through the 1980s. They have been digitized and are accessible through Argentina’s General Archive website, including formerly classified presidential decrees from 1957 to 2005.
The initial online release is organized into seven substantial files, each focusing on major Nazi figures mentioned within them. Among these is a wealth of information regarding Adolf Eichmann, the architect behind the “Final Solution,” which orchestrated the Holocaust. Eichmann lived under the alias Ricardo Klement in Buenos Aires until Mossad agents captured him in a covert operation and transported him to Jerusalem for trial in 1960.
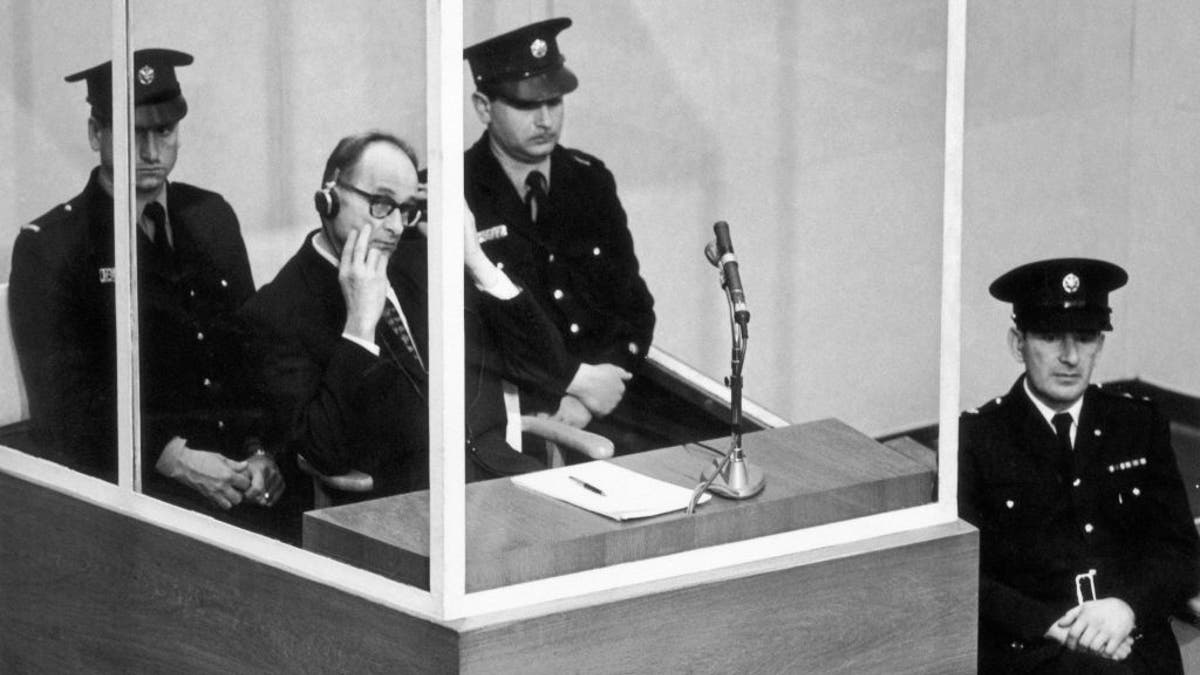

Adolf Eichmann, seen here in a bulletproof booth, listens to the reading of charges against him on December 17, 1961. He was responsible for the genocide of Jews in Poland and later orchestrated the deportation and annihilation of Jews across 13 European nations. (Keystone-France/Gamma-Keystone via Getty Images)
Eichmann’s case is a focal point in these files, revealing conflicting evidence that suggests Juan Perón’s leftist, populist government was not only aware of Eichmann’s presence in Argentina but also took measures to shield him.
Multiple documents also exist detailing the lives of Josef Mengele, the “angel of death” doctor from Auschwitz-Birkenau camps who lived in Argentina and escaped to Paraguay and Brazil, where he died in 1979.
Documents detailing the hunt for Martin Bormann, Hitler’s lieutenant and right-hand man, as well as Croatian murderer, Ante Pavelic, deputy führer and defector Rudolf Hoess and the so-called “butcher of Lyon,” Klaus Barbie, received special attention in the files.
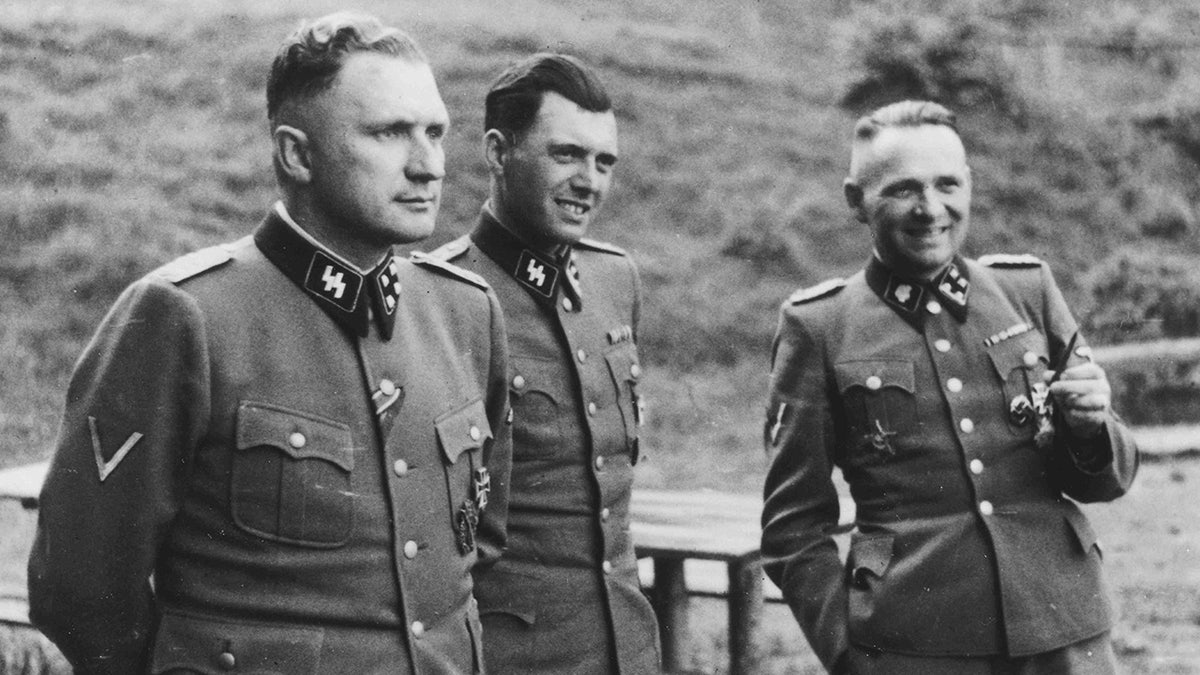

Three SS officers socialize on the grounds of the SS retreat outside of Auschwitz, 1944. From left to right they are: Richard Baer (commandant of Auschwitz), Dr. Josef Mengele and Rudolf Hoess (the former Auschwitz commandant). Mengele escaped to Argentina, later escaping to Paraguay and Brazil. (Universal History Archive/Universal Images Group via Getty Images)
According to Harley Lippman, a member of the United States Commission for the Preservation of America’s Heritage Abroad and a board member of the European Jewish Association, the relevance of the release of the Argentinian documents cannot be understated.
“There are numerous questions that these documents can bring light to, as to why a sophisticated society, far from the plagues of European antisemitism such as Argentina’s, agreed to hide Nazi criminals and their secrets for so long. What happened to the U-boats loaded with Nazi gold brought to the country and given to the authorities?” he asked.
“On the one hand, it is shameful that Argentina kept these documents a secret for so long, but on the other hand, we also need to acknowledge the enormous efforts being made by this government to make these documents public. While the historical significance is important, this is more important for Argentinians to be able to confront their demons as a society than for Jews,” Lippman said.
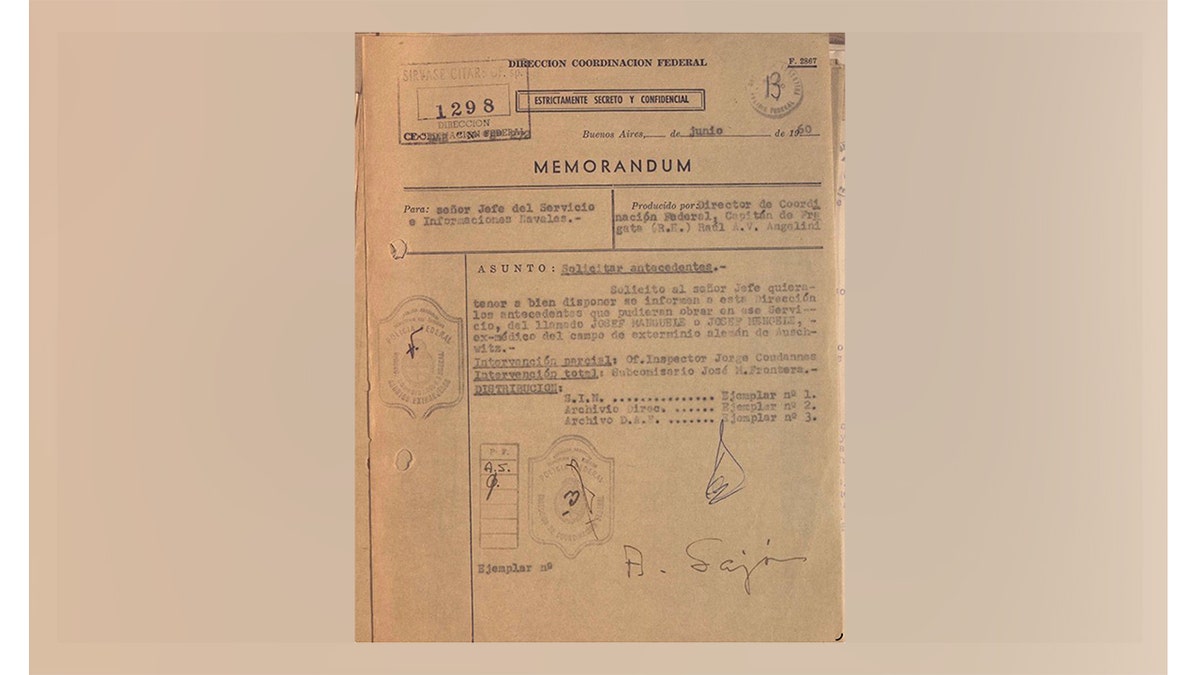
This 1950 Argentine federal police memo, marked strictly secret and confidential, seeks intelligence on Josef Mengele, the notorious Nazi doctor from Auschwitz, suggesting that Argentine authorities were aware of his possible presence or activity in the region at that time. (General Archives of the Government of Argentina)
Adding to the large reveal, in May, while the Supreme Court of Argentina was undergoing renovations and transferring document collections to museums, a forgotten trove of 83 boxes of Nazi documents was discovered almost untouched in the basement of the institution. Upon inspection, the crates revealed documents intercepted by Argentine customs in 1941, sent from the German Third Reich Embassy in Tokyo, Japan, to Argentina’s capital, Buenos Aires, aboard the Japanese steamer Nan-a-Maru.
The documents had been sent as personal effects of embassy personnel but were intercepted under orders of the country’s minister for foreign affairs in order not to undermine Argentina’s neutral position in the war. The shipment became the subject of a probe by a commission investigating “anti-Argentine activities,” which led to the seizure and possession of the crates by the country’s supreme court, where they remained for nearly 84 years.
The finding of the boxes revealed multiple materials intended to propagate and consolidate the Third Reich’s and Hitler’s ideologies in Argentina and South America, possibly in an effort to bring neutral countries under the auspices of Germany.

The document recounts an Argentine police report describing a German fugitive, Walter Flegel, believed by some to be Martin Bormann, Hitler’s former deputy, living under a false identity in Argentina. It was later proven that the lead was incorrect and that Flegal was not Borman. Earlier this year, Argentina President Javier Milei declassified and released over 1,850 documents detailing Argentina’s efforts to track and verify the whereabouts of thousands of Nazi war criminals. (General Archives of the Government of Argentina)
After opening the boxes along with prominent members of the country’s Jewish community, the court issued a statement saying that “given the historical relevance of the find and the potential crucial information it could contain to clarify events related to the Holocaust,” an exhaustive survey of all the material was ordered.
The contents of the crates have not yet been made public, but Milei’s office has said that once all the documents have been digitized, they will also be declassified and made available.
Argentina’s chief of the Cabinet of Ministers, Guillermo Francos, has previously said Milei gave the order “because there is no reason to continue withholding that information, and it is no longer in the interest of the Republic of Argentina to keep such secrets.”
“Jews after World War II lived a golden age of about 80 years where antisemitism had subsided, at least apparently, and they could be productive and contributing members of society. This has now ended — partially because of the genocide committed against Israelis by Hamas on Oct. 7, 2023, with world opinion projecting on Israelis and Jews the false role of perpetrators of genocide in the war in Gaza, but also by bringing back the same old antisemitic views that had been alive in Germany and before then,” Lippman says.
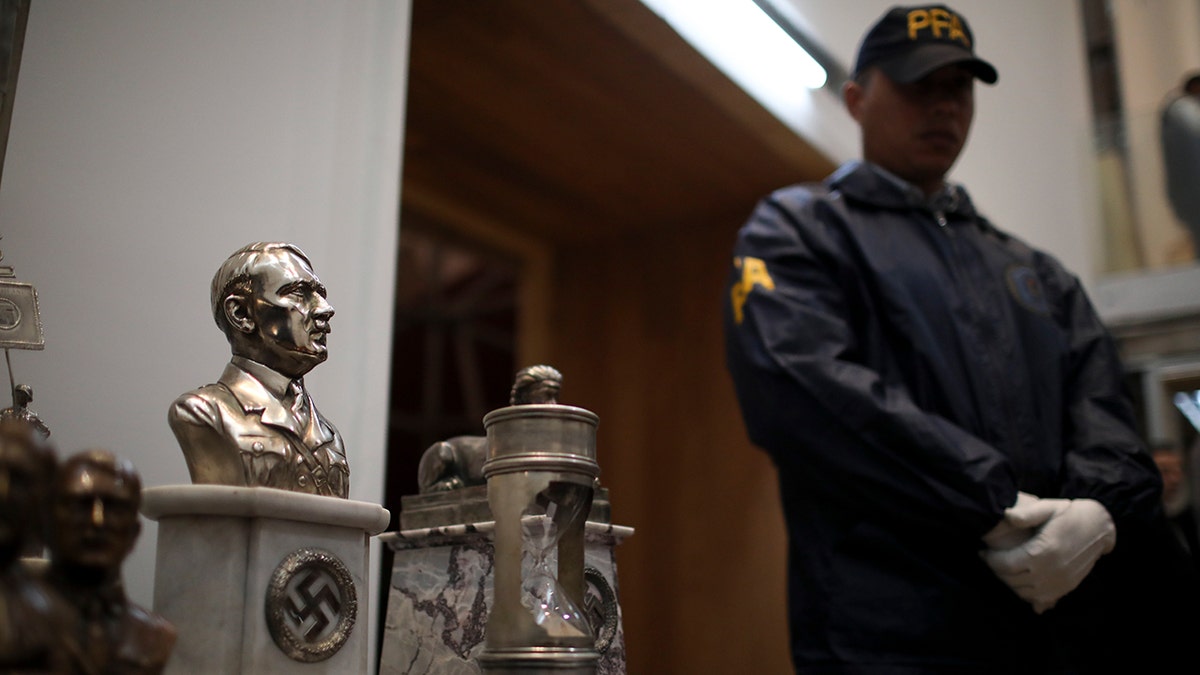

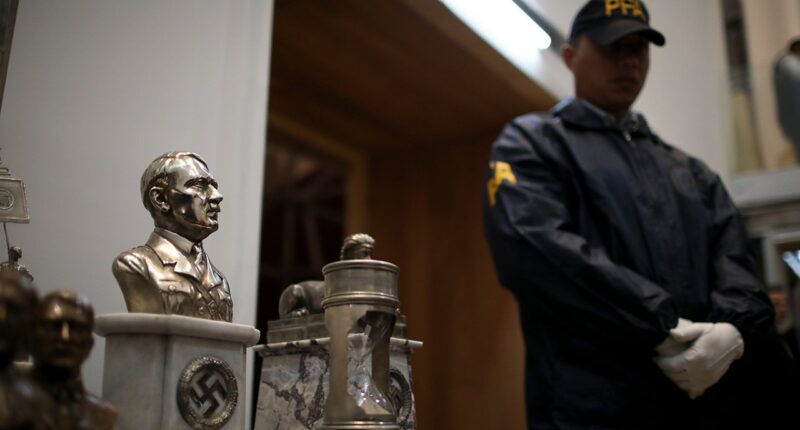
A police officer stands in front of a cache of Nazi artifacts discovered in 2017, during a press conference in Buenos Aires, Argentina, Wednesday, Oct. 2, 2019. Argentine authorities found the cache in a secret room behind a bookcase and had uncovered the collection in the course of a wider investigation into artwork of suspicious origin found at a gallery in Buenos Aires. (Natacha Pisarenko/AP Photo)
“The fact that many people under 30 do not know or understand [the meaning of] the Holocaust is part of the reason why antisemitism is on the rise again. “The Holocaust was the largest systematic industrial killing of humans in history. This happened only 80 years ago. Young people seem not to be able to grasp the scale of this, but these documents can bring back the memory of what the Holocaust really was,” he said, comparing the propaganda war currently faced by Israel and Jews under a progressive and projectionist guise.
Beyond the lives of senior Nazis who escaped to South America on the so-called “ratlines”—possibly under the auspices of certain local governments—Lippman said the documents could also provide important information regarding the role played by Swiss and Argentine banks.
“The Holocaust was the greatest theft in history. Many Swiss banks [which were the depositaries of Jewish money] would not release funds to sometimes a sole survivor from a family who perished in the Holocaust without a death certificate for their loved ones. But Auschwitz did not issue death certificates — they only issued ashes.”

















