Share this @internewscast.com
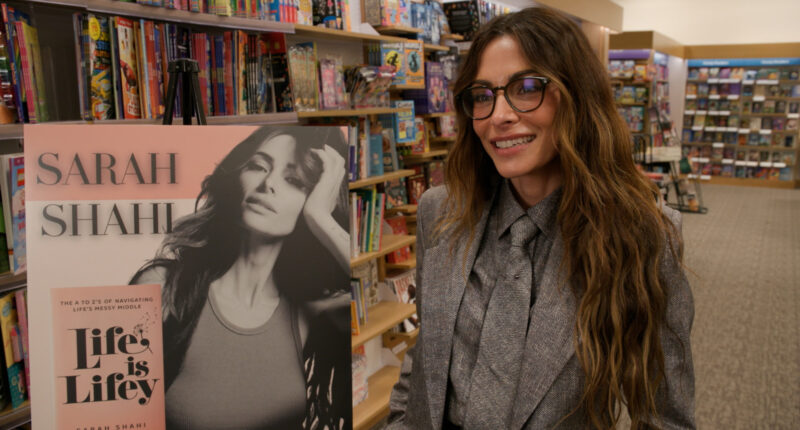
Renowned actress Sarah Shahi is now venturing into the literary world with the launch of her debut book.
The star of “Paradise” has penned “Life is Lifey,” a unique blend of self-help, memoir, and conversational insights aimed at readers seeking inspiration and guidance.
At a recent event in Los Angeles, where her book was celebrated, Shahi shared her journey with On The Red Carpet.
According to Shahi, the inspiration for her book originated during her role in the series “Sex/Life.” In the show, she portrayed Billie, a dissatisfied wife and mother exploring her life’s direction, which resonated deeply with her personal experiences.
She explained, “Playing Billie empowered me to pursue the changes I desired in my own life. Upon the show’s release, I discovered that many women worldwide shared similar feelings. It felt natural to compile all the wisdom and insights I’ve accumulated into one cohesive book.”
Shahi further elaborated, “I wanted to address the full spectrum of life’s challenges. Historically, women were often confined to certain societal expectations and discouraged from seeking more. Writing this book was a healing process for me, and I’m thrilled to find it’s helping others as well. There’s no greater reward than that.”
“I take a lot of inspiration from Nora Ephron. Nora Ephron is a big writing mentor of mine, and the way she constructs a sentiment where you can laugh and cry in the same sentence. And for me, those are the styles in which I am touched the most deeply. And also, I feel like I hate being lectured to. I don’t know anybody who enjoys being lectured to. And so, if I can deliver information and insight in a way that feels humorous, I feel like people will also digest that more. So that was actually a big goal of mine is to write in a that felt very conversational. We were kind of like in our PJs and having a girl chat,” she added.
One quote from the book is that “Courage is something we have to practice,” something Shahi herself had to do in order to get “Life is Lifey” published.
“When I had this idea for this book, I had members of my team at that time…I had five people, five of my representatives back then, who told me I didn’t have a voice, I didn’t know how to write, I didn’t know what I was going to say. I had nothing to say, and if anything, I should wait until I was like 65 and write a memoir. But it really goes to show, and I talk about this in the book too, it’s like being an outlaw for yourself. And for your beliefs,” Shahi said.
Being an outlaw is something that has helped Shahi throughout her career and her life. One such “go against the rules” moment for her was when she emailed creator and showrunner Dan Fogelman in the hopes of getting a role on “This Is Us,” a show she was infatuated with.
“I sent him an email, never heard back. But what’s funny is six months later he offered me a role on another show that he had at the time I said yes only in the hopes of meeting him. I never met him. And might I add, my reps chastised me for this. They were like, ‘you will never work with him because you went behind protocol. You went behind our backs and you did this,’” she explained. “And then cut to the audition for ‘Paradise.’ I walk in the room and the first thing he said was ‘Sarah Shahi, you wrote me an email years ago. I will never forget it. I’ve been wanting to meet you. It’s so nice to finally meet you,’ and I got the role.”
Shahi plays psychotherapist Dr. Gabriella Torabi, who helped Sinatra, played by Julianne Nicholson, create the underground bunker where most of season one took place. Shahi teased what’s ahead in season two for her mysterious character.
“We do learn more about Gabriella and her backstory. And one of the other things on the show is, a lot of the characters, their morals are straddling between good and bad. And last year Gabriella, I felt like she was very altruistic. This year she gets to straddle that line between good and bad and that was fun to do,” she said.
“One of the things about Dan’s writing that I love so much is just when you think you know what’s going on, he has a way of pulling the rug up from underneath you and you actually have no idea what’s happening. And he takes so many of those turns this season and they all pay off in such a huge way that I don’t think anyone would have seen coming.”
“Paradise” season 2 streams on Hulu February 23. And Shahi’s book “Life is Lifey” drops January 27.
The Walt Disney Company is the parent company of Hulu and this ABC station.
Copyright © 2026 OnTheRedCarpet.com. All Rights Reserved.