Share this @internewscast.com

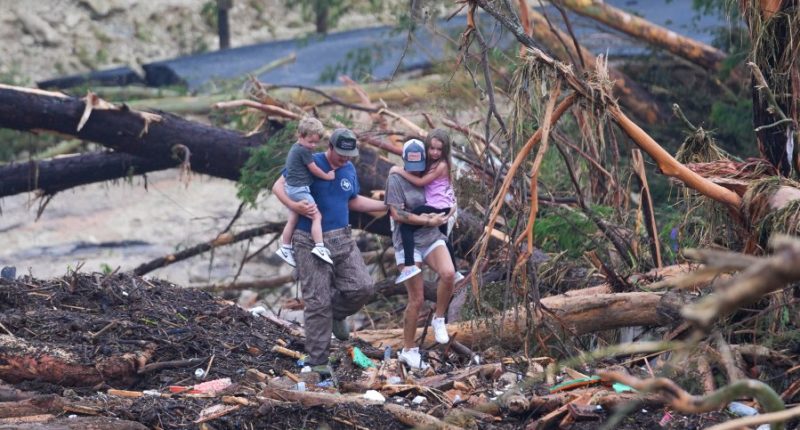
WASHINGTON (AP) — A massive amount of moisture in the atmosphere powered a slow-moving storm that produced heavy rainfall over central Texas, leading to deadly flash floods in the early hours when people were unsuspecting, say meteorologists.
Over 12 inches (30 centimeters) of rain drenched the Texas Hill Country in just a few hours early Friday, swiftly escalating water levels, according to AccuWeather. The region is naturally susceptible to flash flooding, but this storm was particularly severe, striking during the perilous overnight period, experts noted. Reports indicate numerous fatalities and many rescue operations have been undertaken.
Experts explained that with human-induced climate change heating the atmosphere, more moisture is retained, which can intensify storms and result in heavier rainfall, though it remains challenging to directly associate individual storms with climate change immediately after their occurrence.
“In a warming climate we know that the atmosphere has more moisture to give, to hold on to and then to release. But also the thing that we know about climate change is that our rain events are not as uniform as what they used to be,” said Shel Winkley, a meteorologist with Climate Central. “So, you’ll get these big rain events happening in localized areas, tapping into the historic level of moisture in the atmosphere.”
In recent weeks, flash flooding driven by bursts of heavy rain turned deadly elsewhere in Texas and in West Virginia. In San Antonio in June, more than 7 inches (18 centimeters) of rain fell over a span of hours, prompting dozens of rescues from the fast-rising floodwaters and killing at least 13. And in West Virginia that month, at least nine people died when as much as 4 inches (10 centimeters) of rain fell within 40 minutes and caused flash flooding in the Wheeling area.
Staggering rain runs off hard ground
Robert Henson, a meteorologist and writer with Yale Climate Connections, said this latest Texas rain storm was roughly a once-in-a-generation event. It fell in the Texas Hill Country where water quickly shoots down rugged hills into narrow river basins that swell quickly.
“As is often the case with the worst disasters, many things came together in a terrible way.” Henson said.
Plus, the area had been in a drought, so the water ran down the dry, hard land fast. That made it more dangerous for children attending camp.
“A sudden surge of rain like that is going to have a harder time getting absorbed,” said Brett Anderson, a senior meteorologist at AccuWeather. “It just runs right off of it. It’s like concrete.”
The sheer amount of rain was overwhelming. Former NOAA chief scientist Ryan Maue, a private meteorologist, calculated Saturday morning that the storm had dropped 120 billion gallons of water on Kerr County, which received the brunt of the storm.
A storm with plenty of fuel
Moisture fueled the storm from many directions. Tropical Storm Barry formed briefly last weekend, moving over Mexico and then its remnants continued up into Texas. But the jet stream, a current of air that moves weather patterns, wasn’t there to push that moisture away.
“Normally weather systems and the remnants of tropical systems will get picked up by the jet stream, and that’s just not over Texas currently,” said Winkley, the Climate Central meteorologist. “It’s essentially a weather system without a road to get away from the Lone Star State.”
The warm water of the Gulf fueled the moist atmosphere. Even more moisture came from areas over the Pacific Ocean to the west. The combination gave the storm plenty of fuel once it got started.
Winkley said in the area that flooded, climate change might mean that rain storms are less common, but when they do occur they can be more severe.
Generally a warmer atmosphere can hold more moisture, creating conditions for storms to drop more rain.
“With climate change we have a warming atmosphere. A warmer atmosphere holds a lot more moisture, and we are seeing obviously much more total atmospheric moisture across the globe in recent years than we normally have,” said Anderson, the AccuWeather meteorologist.
___
The Associated Press receives support from the Walton Family Foundation for coverage of water and environmental policy. The AP is solely responsible for all content. For all of AP’s environmental coverage, visit