Share this @internewscast.com
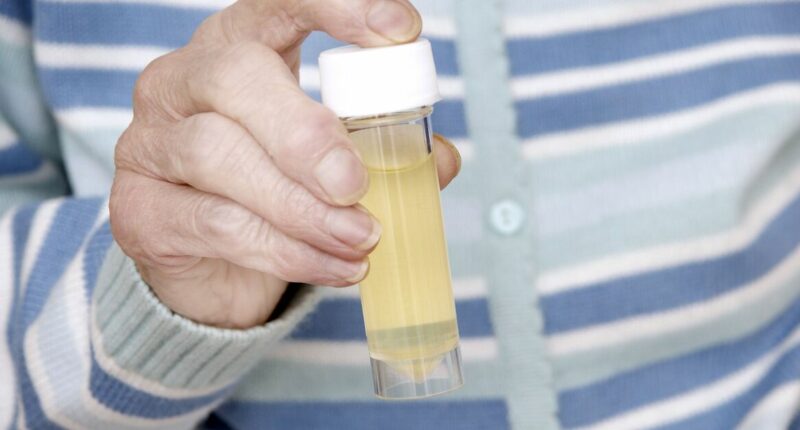
A new study suggests that a simple urine test could identify your risk of developing dementia, potentially decades before any symptoms manifest. Conducted by researchers at Sweden’s Karolinska Institute, the study involved tracking 130,000 individuals and discovered that protein in the urine may serve as an “early warning sign for memory problems.”
The research found that elevated levels of protein in urine, a condition known as albuminuria, significantly increased the likelihood of developing dementia. This correlation was most pronounced for vascular dementia, the second most prevalent type after Alzheimer’s, and mixed dementia, which involves elements of both forms. Importantly, this connection remained significant regardless of the overall kidney function of the participants.
According to Hong Xu, an assistant professor at the Division of Clinical Geriatrics at Karolinska Institutet, who led the research, “Our findings highlight how closely the kidneys and brain are connected.”
“Both organs depend on networks of tiny, delicate blood vessels to operate correctly. Damage to these vessels – due to high blood pressure, diabetes, or other factors – can cause protein to leak into urine and also diminish blood flow to the brain,” Xu explained.
“Kidneys act like filters, retaining useful proteins in the blood while eliminating waste. When these filters sustain damage, albumin protein begins to leak through,” he added.
“The brain is protected by its own barrier – the blood-brain barrier – consisting of tightly packed cells that prevent harmful substances from entering brain tissue.”
“Just as damaged kidney filters become leaky, a compromised blood-brain barrier allows toxins and inflammatory molecules to pass through, potentially triggering the brain changes that lead to dementia.”
This discovery opens exciting possibilities for prevention.
Hong Xu says several medications already used to protect kidneys may also protect memory and ‘weight loss jabs’ developed to combat diabetes also reduce protein in urine – which could indicate they help to prevent dementia.
She said: “While we cannot yet prove that treating kidney problems will prevent dementia – that would require following participants for decades in controlled trials – the biological pathway makes sense, particularly given how blood vessel damage affects both organs.”
So when should you start caring about this? Vascular damage accumulates over years, so earlier intervention is better
Hong Xu said lifestyle changes that protect kidneys also benefit the brain – quitting smoking, controlling blood pressure and blood sugar, eating a balanced diet and exercising regularly can reduce your risk of both kidney disease and dementia.
She adds: “For most people, focusing on kidney and heart health from middle age onwards is sensible, especially if you have diabetes, high blood pressure, kidney disease, obesity, or a family history of these conditions.
“Currently, doctors mainly test urine protein in people with diabetes or high blood pressure. But our findings raise questions about whether everyone over 50 should be screened, particularly those with multiple risk factors.
“That is a public health question requiring more research and policy discussion.
“The good news is that you do not need to wait for new guidelines to take action. Lifestyle changes that protect kidneys also benefit the brain.
“Quitting smoking, controlling blood pressure and blood sugar, eating a balanced diet and exercising regularly can reduce your risk of both kidney disease and dementia.
“If confirmed by future studies, urine protein testing could become a standard part of dementia risk assessments. It is cheap, non-invasive and can be performed with simple dipstick tests in any doctor’s office.
“While there is still no cure for dementia, early detection and prevention remain our best tools. By recognising that protein in urine signals more than just kidney trouble, we may be able to identify and protect those at risk long before memory problems begin.
“Sometimes the most important clues about your brain’s future health are found in the most unlikely places.”