Share this @internewscast.com

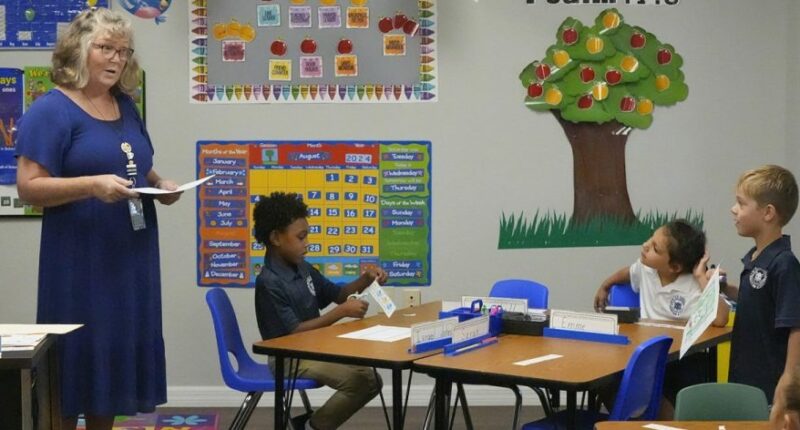
Babies born at the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic are now making their way into preschool and kindergarten, leaving experts eager to observe the pandemic’s influence on these young learners.
There’s growing concern over potential cognitive and social delays, such as struggles with sharing or following directions, amid mixed research findings and educators’ observations about 4- and 5-year-olds.
While older students showed immediate adverse effects during the pandemic, the long-term impact on those born during this period remains uncertain. Experts emphasize the need for educators to stay watchful in the upcoming school year.
A recent study in the journal Infancy examined data from 330 infants born between October 2016 and August 2021, revealing minimal differences in negative effects pre- and post-pandemic. It indicated that higher negative impacts were more linked to factors like maternal stress.
Pandemic-related stress increased significantly for caregivers due to job losses and reduced social interactions, with varying effects based on family income levels.
“Children from higher socioeconomic backgrounds have actually shown developmental improvements,” noted Rahil Briggs, national director of Zero to Three’s HealthySteps program. “Caregivers might have been home more, providing more time, attention, support, shared family meals, and reading, which are crucial for development.”
Another study found that the lower the socioeconomic background, “the more that decrease in kindergarten readiness showed up,” she added.
But other studies showed more differences between the youngest learners before and after COVID-19, including a higher risk for social, cognitive, communication, motor and social delays among those born during the height of the pandemic.
A study released in 2024 that examined a cohort of 3.5- to 5.5-year-olds found after the pandemic this age group tested “significantly worse on several measures of false-belief understanding.”
“So for things to be affecting the kids now, it really has to be something that made a fundamental shift in their development those first couple of years and that can happen. We do know that the first three years of life are super important. What we haven’t had is something that hits us over the head yet beyond anecdotal,” said Koraly Pérez-Edgar, a professor of psychology at the Pennsylvania State University.
Pérez-Edgar cited a New York Times story from July 2024 that indicated “the kids going into kindergarten last year were really messed up, or, like, really had a lot of trouble.” But she said such behavior hasn’t been borne out in studies yet.
“It’s not showing up in the data quite as strongly or quite as forcefully as some of the anecdotal reports say,” adding the concerns experts are worried about likely won’t emerge or be discovered until they are in school.
Older kids had immediate effects that were easy to see when the pandemic closed schools in 2020 and created restrictions in classrooms in 2021.
Behavioral problems in classrooms, chronic absenteeism and anxiety went up, while academic performance went down in older students, with some of those effects still lingering today.
But infants had time to live in a world without masks and restrictions for years before heading to kindergarten.
“So, the pandemic was 2020, five years ago, and things really the last three years, they would have had the opportunity to have a pretty normal socialization for most kids,” said Eileen Kennedy-Moore, a psychologist and podcast host of “Kids Ask Dr. Friendtastic.” “So, I don’t think we have to assume that because of COVID these kids are warped. I think we deal with the child in front of us.”
Experts and advocates caution vigilance and advise planning for a situation where these children begin to struggle in school, such as smaller class sizes and collaboration with families.
“We think a lower group size or maybe additional adult support in the classroom, like a teacher’s aide, could be helpful for kindergarten programs. I do think significant family engagement is going to be really helpful to support these young children and families,” said Ginger Sandweg, senior director early learning at First Things First.
But experts also note it is important to recognize children are able to bounce back from adversity well, even if some struggles occurred after the pandemic with socialization.
“I think if schools are aware of these particular areas, they can do more programming in terms of teaching kids like asserting yourself and talking, having conversations,” said Mary Alvord, psychologist and founder of Alvord, Baker & Associates.
“But my area is resilience, and I just feel like we also need to acknowledge the resilience of most kids,” she added.