Share this @internewscast.com

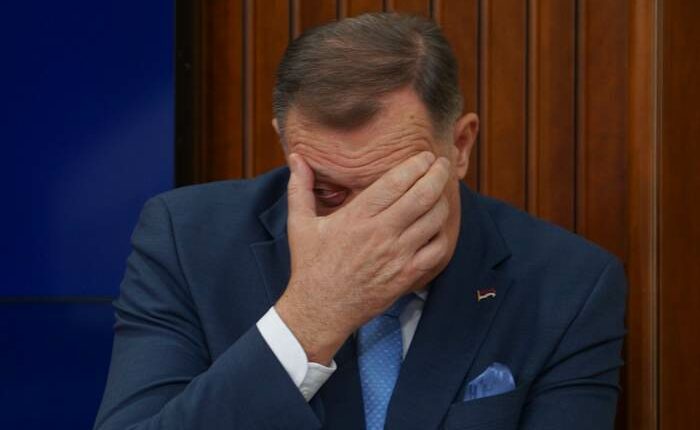
SARAJEVO – The electoral authority in Bosnia has removed Milorad Dodik from his role as president of the Serb entity within Bosnia. This decision follows a court ruling sentencing Dodik to a year in prison and barring him from political activity for six years.
The Central Electoral Commission has stated that Dodik can appeal this decision, and if upheld, a new presidential election will occur within 90 days. The previous election for the Bosnian Serb president took place in 2022.
Dodik’s legal team plans to request a delay in executing the verdict and will appeal to the Constitutional Court of Bosnia-Herzegovina.
The appeals court in Bosnia-Herzegovina upheld a previous decision sentencing Dodik, a pro-Russian Bosnian Serb leader, to prison with an additional six-year restriction on political engagement. This led to the cancellation of his presidency.
Dodik has dismissed the court’s decision, asserting he will remain in his role as president with backing from the Bosnian Serb parliament. His stance is supported by Serbian President Aleksandar Vucic and Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orban.
The Bosnian Serb government said it does not accept the court ruling because it is “unconstitutional and politically motivated.”
The speaker of the Bosnian Serb parliament, Nenad Stevandic, commented, “We cannot imprison him, that’s impossible. We can’t prevent him from engaging in politics. He will continue with his activities as before.”
The European Union said last week that the “verdict is binding and must be respected.” Bosnia is a candidate for EU membership but has been told by Brussels to strengthen the rule of law. Dodik’s separatist and pro-Russian activities stalled Bosnia’s progress toward EU membership.
Dodik has repeatedly called for the separation of the Serb-run half of Bosnia to join Serbia, prompting the former U.S. administration to impose sanctions against him and his allies. Dodik was also accused of corruption and pro-Russia policies.
Dodik’s separatist threats have stoked fears in Bosnia, where a 1992-95 war erupted when the country’s Serbs rebelled against independence from the former Yugoslavia and moved to form a ministate with the aim of uniting it with Serbia. About 100,000 people were killed and millions were displaced.
The U.S.-sponsored Dayton Accords ended the war and created two regions in Bosnia, Republika Srpska and the Bosniak-Croat Federation, which were given wide autonomy but kept some joint institutions, including the army, top judiciary and tax administration. Bosnia also has a rotating three-member presidency made up of Bosniak, Bosnian Serbs and Bosnian Croats.
Dodik has repeatedly clashed with the top international envoy overseeing the peace, Christian Schmidt, and declared his decisions illegal in Republika Srpska. The Dayton peace agreement envisages that the high representative can impose decisions and change laws in the country.
——
Associated Press writer Dusan Stojanovic contributed from Belgrade, Serbia.
Copyright 2025 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without permission.