Share this @internewscast.com
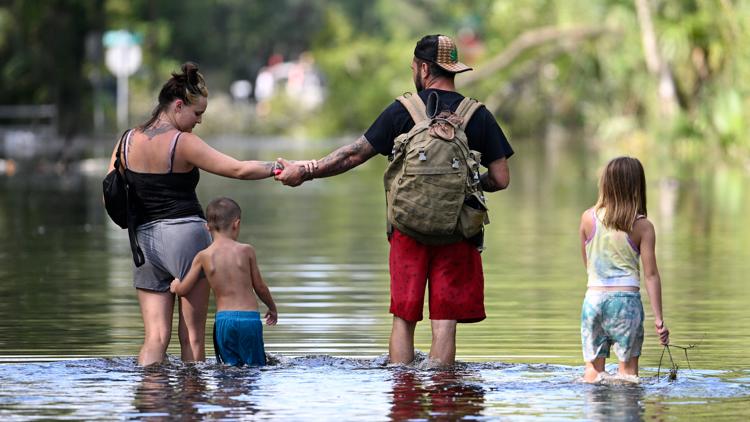

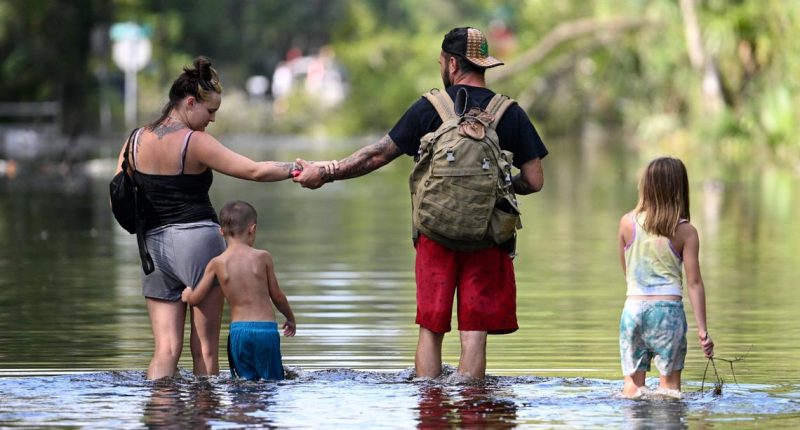
Hurricane season runs from June 1 to November 30 and is predicted to busier than average this year.
WASHINGTON — As the hurricane season begins on Sunday, experts in meteorology and disaster management are expressing concern about issues that could be as problematic as the storms themselves: Significant reductions to the federal framework for forecasting, tracking, and managing hurricanes.
Alarm is spreading among experts due to the substantial cuts in staff, restricted travel and training, and cessation of grants since President Donald Trump’s administration took charge, affecting both the Federal Emergency Management Agency, which handles hurricane preparedness and response, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, responsible for storm tracking and forecasting.
“My fear is a major catastrophic storm striking an area already struggling due to these detrimental changes from the Trump administration, leading to loss of life. This scenario could unfold in Florida, Texas, or South Carolina,” said Susan Cutter, the head of the Hazards and Vulnerability Research Institute at the University of South Carolina.
Representatives of both NOAA and FEMA say the agencies are prepared.
About 2,000 full-time staff have left FEMA since Trump took office in January, a loss of roughly one-third of the agency’s full-time workforce, amid Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) mandated cuts. Scholars who study emergency management are concerned by both the reduction in capacity and the “brain drain” of experienced staff.
“There’s really been a brain drain within FEMA in addition to the loss of overall employees,” said Samantha Montano, who teaches emergency management at the Massachusetts Maritime Academy. She noted that many who left were in critical management positions.
The agency is run by an acting chief, David Richardson, a former Marine Corps officer who served overseas and worked as the Department of Homeland Security’s assistant secretary for countering weapons of mass destruction. He does not appear to have any experience in managing disasters. Emergency management requires knowing where to get things, who to call, how things work and how to get it done quickly — which comes from experience and establishing relationships with state officials, Montano and Cutter said.
What’s happening reminds former Federal Emergency Management Agency Director Craig Fugate of 2005, the year Hurricane Katrina devastated Louisiana and exposed inexperienced and poorly prepared governments at all levels, especially the then-FEMA chief who came from a horse-rearing association. Fugate said he’s especially worried about top experienced disaster people leaving FEMA.
FEMA canceled various emergency management trainings this spring, moved others online and restricted travel to events such as the National Hurricane Conference. Some trainings have resumed.
“Given the reduction in staffing, being unable to do trainings, participate in conferences, there’s potential that the federal government’s ability is diminished,” said former Florida Emergency Management chief Bryan Koon, now president of the disaster preparedness firm IEM.
FEMA has also cut disaster resilience programs. Making areas more survivable saves up to $13 for every dollar spent, said Lori Peek, director of the Natural Hazards Center at the University of Colorado.
The federal government promises to be ready for hurricane season, which runs through November.
“FEMA is shifting from bloated DC-centric dead weight to a lean, deployable disaster force that empowers state actors to provide relief for their citizens,” Associate FEMA Administrator Geoff Harbaugh said in a email. “FEMA is fully activated in preparation for hurricane season.”
Richardson promised to push more responsibilities to the states. He warned that the agency will only do what the law requires and shift more costs to states.
But Koon noted that states haven’t budgeted for FEMA’s changes, adding: “The biggest issue right now is just the uncertainty.”
Some states — which coordinate disaster operations — are experienced in catastrophes, have well trained staff and will do fine, such as Texas and Florida, Fugate said. But it’s the poorer states that worry the experts.
The feds often pick up the entire bill in big disasters and most of it in smaller ones. In the Trump administration, disaster declarations have been denied or delayed. When disaster declarations were issued for nine states last week, some had been pending for two months and others were only partially approved.
“We’ve just relied on FEMA for so much for so long and not knowing who’s going to fill the gap and how we’re going to fill it is really scary,” said University at Albany emergency management professor Jeannette Sutton.
NOAA, the parent agency of the National Weather Service, has undergone a series of dramatic job cuts, with some people then reinstated. A sizable chunk of the weather service’s 121 local field offices as of late March had vacancy rates of more than 20%, what’s seen by outsiders as a critical level of understaffing. Local weather offices are crucial in helping people translate national warnings into what to do locally.
“It should be all hands on deck and we’re being hollowed out,” former NWS director Louis Uccellini said.
But the National Hurricane Center, which tracks and warns of hurricanes in the Atlantic, Pacific and Caribbean, has been spared. Acting NOAA Administrator Laura Grimm, National Weather Service Director Ken Graham and National Hurricane Center Director Michael Brennan said the agency is prepared for the season with the Miami-based storm center fully staffed and so are the planes that fly into storms.
For the first time this year, the hurricane center will incorporate artificial intelligence into forecasting because it has shown to improve predictions generally, Brennan said.
“Our services have never been better,” Graham said. “Our ability to serve this country has never been better. And it will be this year as well.”
But beyond the hurricane center, weather balloons launches have been curtailed because of lack of staffing. In some places, balloon launches have dropped from twice a day to once a day.
NOAA hopes to get more balloons launched if needed, Brennan said.
Data from the balloons is crucial for understanding steering currents and needed for forecasts, Uccellini said. He said when hurricanes threatened during his tenure he would order the launch of several extra balloons in the Great Plains to help figure out if storms would hit the United States.
“Hurricane forecasts, I’m expecting not to be as accurate this year because of that lack of balloon data,″ said former NOAA meteorologist Jeff Masters, now at Yale Climate Connections.
Aoun Angueira reported from San Diego.
Copyright 2025 Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed.