Share this @internewscast.com
NAPA, Calif. – The U.S. wine industry is grappling with the far-reaching effects of tariffs on imported goods, which are impacting both the importation of wine and domestic wine production, according to industry experts.
“Tariffs present a complex problem,” explained Dawson Hobbs, executive vice president of government affairs at the Wine and Spirits Wholesalers of America. “While most people immediately think about tariffs on imported wine, there are numerous hidden factors. Tariffs on essential items like glass, aluminum cans, labels, and even the glue used for packaging significantly impact the entire production process and supply chain.”
Wholesalers, who serve as intermediaries by purchasing products from producers or importers and selling them to retailers, are also facing increased financial pressures. The costs associated with holding inventory have risen, meaning these expenses either need to be passed on to retailers or absorbed by the wholesalers themselves.
“As our costs increase, so do the expenses related to keeping products in our warehouses,” Hobbs noted. “This creates substantial challenges for the entire industry and its supply chain.”

Adding to the complexity is the unpredictable nature of tariff announcements. Earlier this year, the Trump administration initially threatened to impose 200% tariffs on European wine imports, before ultimately deciding on a 15% tariff.
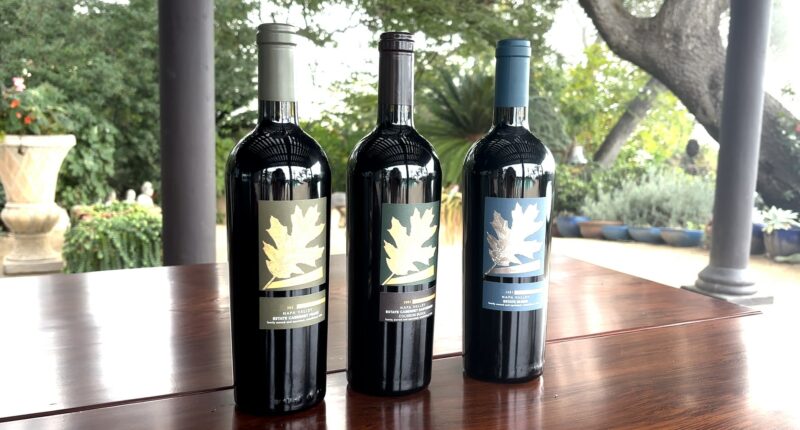
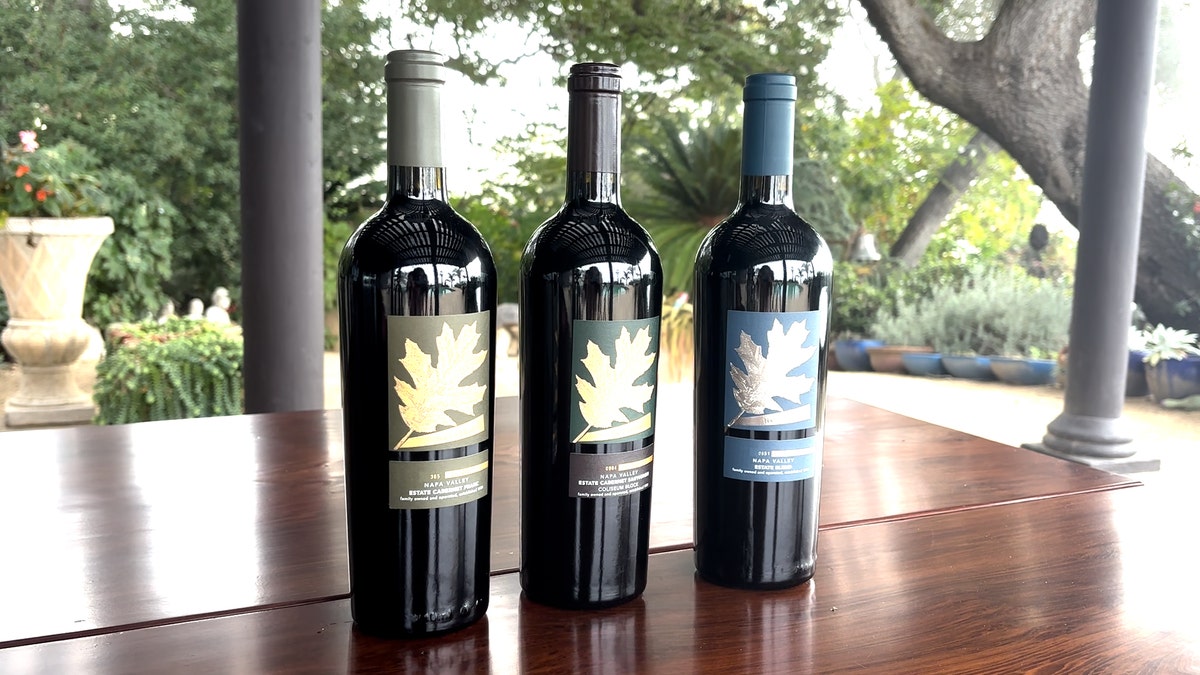
A snapshot of the impact can be seen with three bottles of Hossfeld Vineyards wines elegantly displayed on a table, a visual reminder of the industry’s ongoing challenges. (Photo by Amalia Roy)
“At the beginning of the year, there were tariffs threatened, then delayed, then implemented. When products take 60 to 70 days to arrive, it’s very difficult to plan when you don’t know what the tariff rate will be,” Hobbs told Fox.
Hobbs warned that rising costs could soon affect consumers more directly.
“Many companies have tried to absorb the cost, but as we near the end of this year and into the beginning of next year, consumers will start to see the impact on shelf prices,” he said.
Tariffs can affect American producers indirectly, when many components involved in wine production come from overseas.
“American wines are certainly feeling tariffs in terms of inputs, aluminum cans, glass, cardboard, glue,” Hobbs said. “But overall, it creates more headwinds for the industry and does not help anyone with the final experience for the consumer.”
Lucia Hossfeld, co-owner of Hossfeld Vineyards with her husband, said they are feeling the effects of tariffs on the winemaking side of the business.
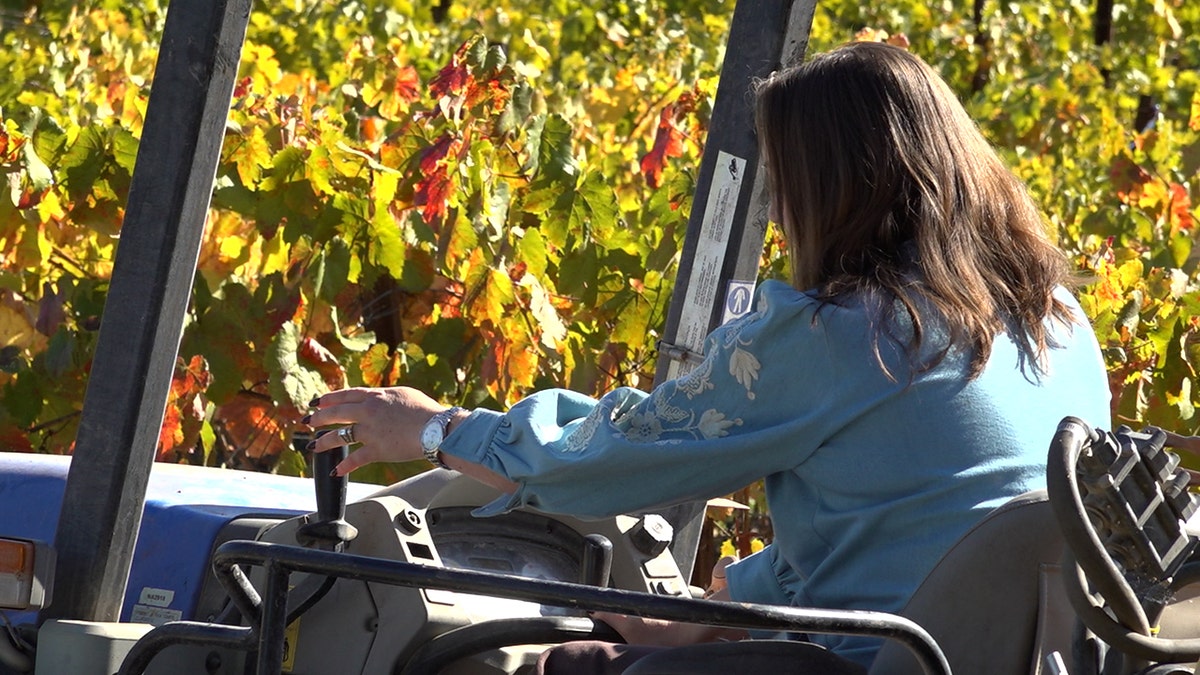

Lucia Hossfeld operates a tractor on her vineyard. (Amalia Roy)
“French oak barrels, the glass bottles, the cork. We’ve also seen consolidation, the labeling of the wine, as well as the selling of the wine. We’ve seen kind of retaliatory tariffs,” Hossfeld said.
It is often difficult to source some of the needed materials in the United States, she explained. Other times, certain imported materials are necessary for the type of wine they make.
Over the last 18 months, costs have risen around 20%, largely due to inflation and labor costs, but tariffs implemented earlier this year have also added to higher operational expenses. Hossfeld said they’re working with trade partners to absorb costs and keep prices stable.
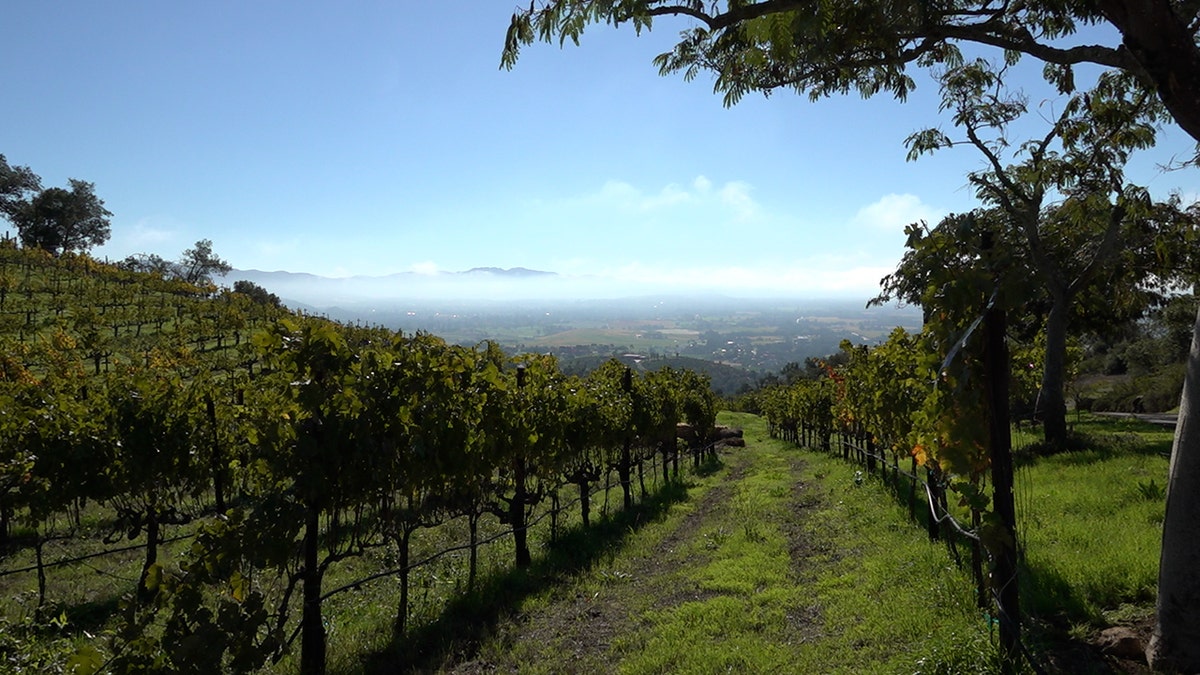

The view from Hossfeld Vineyards in Napa, California, overlooking the Napa Valley. (Amalia Roy)
“On the supplier end, our barrel company, they’re making concessions, you know, splitting the cost with us,” Hossfeld said.
Similarly to domestic winemakers, Hobbs said many wholesalers are also absorbing the cost of tariffs, but he warned it’s not a sustainable solution.
“Our industry has very thin margins for the most part. Most people that you talk to do believe you will start seeing real price increases, unfortunately, as we near Christmas, and as we get into the first of the year,” Hobbs said.