Share this @internewscast.com

KERRVILLE, Texas (AP) — Emergency responders halted their search for individuals affected by the severe flooding in central Texas on Sunday morning due to fresh alerts predicting that more rain would once again cause rivers to overflow.
It was the first time a new round of severe weather has paused the search since the flooding earlier this month.
The Ingram Fire Department instructed their search teams to leave the Guadalupe River area in Kerr County at once, as there is a significant risk of a flash flood. Rescue operations had been underway to locate those missing from the flooding over the July 4 weekend.
Search and rescue efforts were expected to resume on Monday, depending on river flow, Fire Department spokesman Brian Lochte said.
“We’re working with a few crews and airboats and SAR (search-and-rescue) boats just in case,” Lochte said.
As heavy rainfall persisted on Sunday, forecasters from the National Weather Service alerted that the Guadalupe River might climb nearly 15 feet (4.6 meters) by Sunday afternoon, exceeding flood stage by about five feet, enough to submerge the Highway 39 bridge near Hunt.
“Numerous secondary roads and bridges are flooded and very dangerous,” a weather service warning said.
The destructive, fast-moving waters rose 26 feet (8 meters) on the Guadalupe River in just 45 minutes before daybreak on July 4, washing away homes and vehicles. Ever since, searchers have used helicopters, boats and drones to look for victims and to rescue people stranded in trees and from camps isolated by washed-out roads.
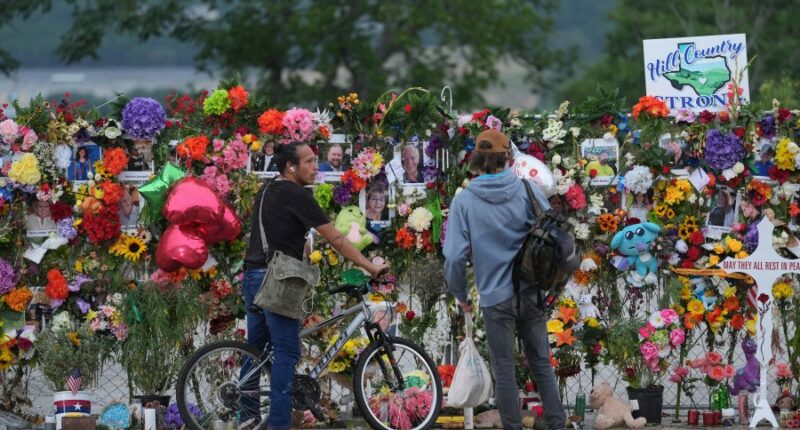
The floods laid waste to the Hill Country region of Texas. The riverbanks and hills of Kerr County are filled with vacation cabins, youth camps and campgrounds, including Camp Mystic, the century-old all-girls Christian summer camp.
Located in a low-lying area along the Guadalupe River in a region known as flash flood alley, Camp Mystic lost at least 27 campers and counselors and longtime owner Dick Eastland.
The flood was far more severe than the 100-year event envisioned by the Federal Emergency Management Agency, experts said, and moved so quickly in the middle of the night that it caught many off guard in a county that lacked a warning system.
The sheer amount of rain was overwhelming. Former NOAA chief scientist Ryan Maue, a private meteorologist, calculated on July 5 that the storm had dropped 120 billion gallons of water on Kerr County, which received the brunt of the storm.
This summer, flash flooding driven by bursts of heavy rain turned deadly elsewhere in Texas. In San Antonio in June, more than 7 inches (18 centimeters) of rain fell over a span of hours, prompting dozens of rescues from the fast-rising floodwaters and killing at least 13.