Share this @internewscast.com
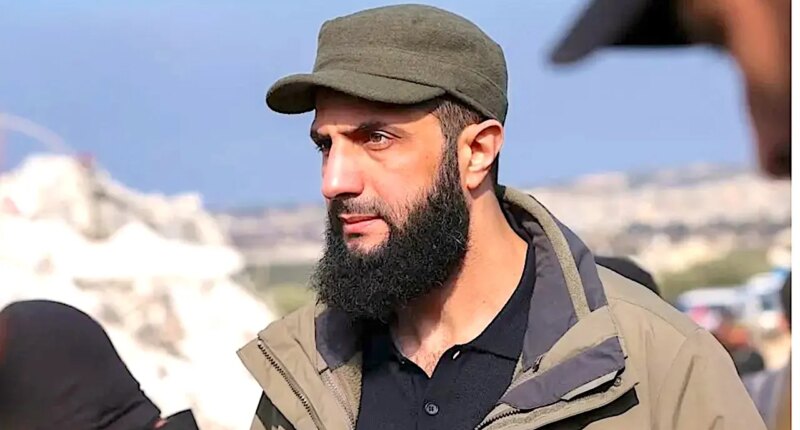
Formerly affiliated with al Qaeda and the Islamic State, Ahmed al-Sharaa is now at the forefront of Syria’s delicate transition following the ousting of the Bashar Assad regime. He is preparing to address the world at the United Nations General Assembly on Wednesday, aiming to present his vision for Syria’s future.
“This is the first time since 1967 that a Syrian president will participate in high-level meetings at the United Nations General Assembly, making it a significant event,” said Natasha Hall, a senior associate at the Center for Strategic and International Studies, in an interview with Fox News Digital.
“During this historic moment, al-Sharaa will likely stress that he represents a new era for Syria, having overthrown Assad’s oppressive dictatorship. He will highlight the progress made and discuss the additional steps needed for international recognition and the removal of U.N. sanctions to aid Syria’s progress,” Hall explained.
Rose, who visited Syria earlier this year, observed that the country’s intricate political environment has not only caused a standstill but has also limited its ability to respond in crises. This includes incidents like failing to control radical Sunni fighters during violent surges in Latakia and Suwayda. Additionally, policies catering to more traditional segments of al-Sharaa’s support base, such as enforcing full-body swimwear at Syrian swimming locations, have been noted.
While the new Syrian government strives to exert control over a divided populace, Shara’s administration must navigate a fragile society characterized by ethnic and religious fractions.
Syria has been embroiled in sectarian violence since the uprising against Assad. Government forces responded in force when pro-Assad factions attacked in Latakia, Assad’s birthplace. The U.N. reports that around 1,400 individuals, predominantly civilians including Alawites, a minority group Assad belonged to, and members of the Druze community, were massacred.
It was the worst episode of violence since the overthrow of Assad in December 2024.
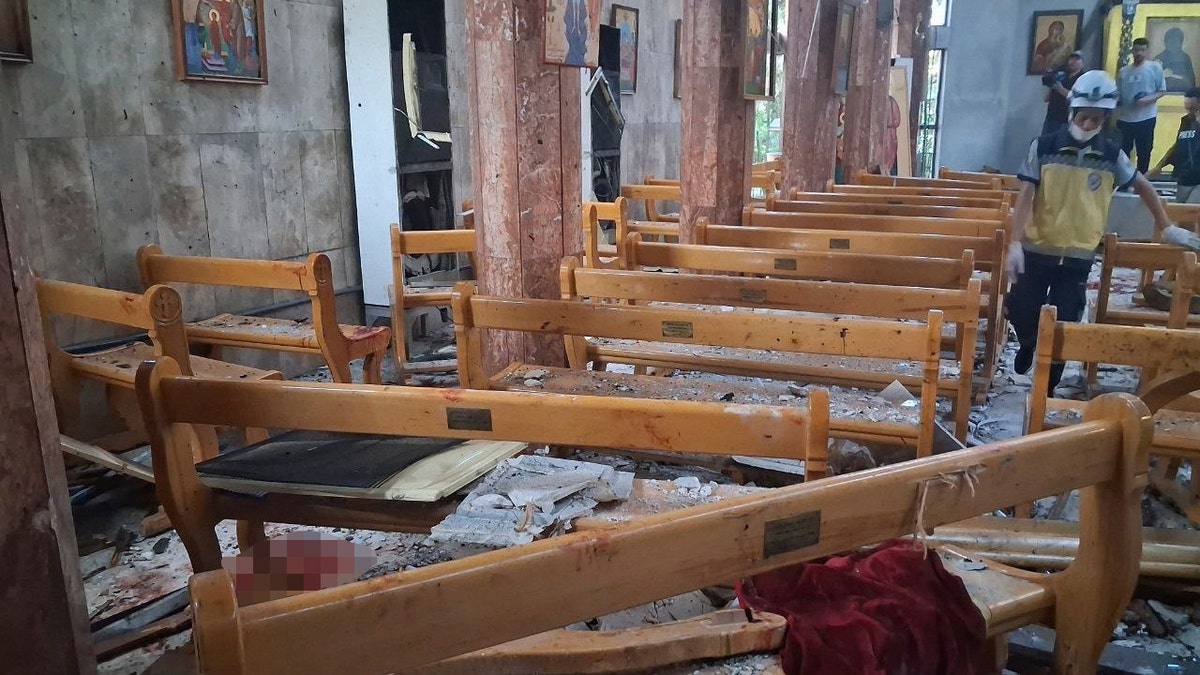

In this photo released by the Syrian official news agency SANA, a Civil Defense worker inspects the damage inside Mar Elias church where a suicide bomber detonated himself in Dweil’a on the outskirts of Damascus, Syria, Sunday, June 22, 2025. (SANA via AP)
Clashes between Bedouin tribes, Druze militias and government forces in Suweida led to hundreds of deaths and drew in Israeli military intervention — to protect Syria’s Druze minority. A ceasefire was eventually agreed to but the spiraling ethnic violence highlights Syria’s rocky transition.
The country’s dwindling Christian community has also felt the brunt of extremist violence. In June, the Islamic State was suspected of carrying out a deadly suicide bombing at a Greek Orthodox church in Syria, which killed 22 worshipers and injured 63 others. Christians have also been attacked and, in some cases, killed, allegedly by forces tied to the al-Sharaa government.
The new authorities will also have to incorporate Kurdish forces operating in Northeast Syria, where the Syrian Democratic Forces have been crucial to the U.S.-led counter-ISIS campaign. Any disruptions in the merging of the SDF into the Syrian state raises the risk of an ISIS resurgence.