Share this @internewscast.com

(KTXL) A resident of South Lake Tahoe, California, has tested positive for the plague, health officials have confirmed.
Limited information has been disclosed about the resident, but the El Dorado County Environmental Management Division and Public Health Division stated that the individual is receiving medical care while recuperating at home.
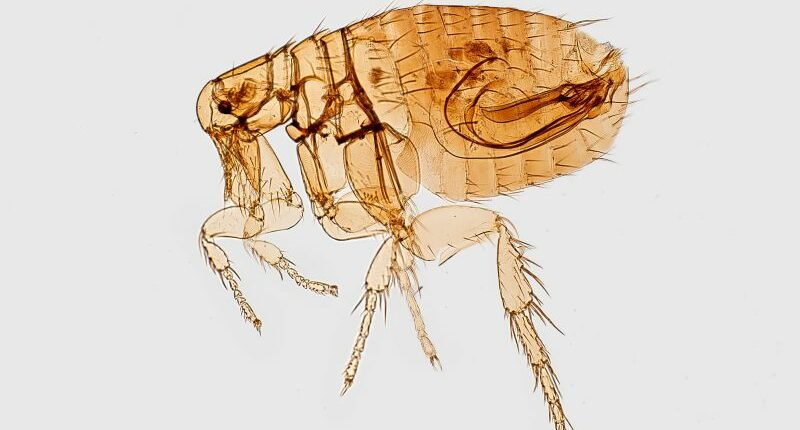
The case is still being examined. It is suspected that the individual fell ill due to a flea bite while camping in the South Lake Tahoe region.
“Plague naturally exists in several regions of California, including the elevated areas of El Dorado County,” noted Kyle Fliflet, Acting Director of Public Health for El Dorado County. “It’s crucial for people to take precautions for themselves and their pets when spending time outdoors, particularly when walking, hiking, or camping in areas where wild rodents are present.”
The plague is caused by the Yersinia pestis bacterium, which is primarily spread through flea bites from fleas that have acquired the bacteria from infected squirrels, chipmunks, and other wild rodents. Pets such as dogs and cats can also carry plague-infested fleas into the home, health officials warn. Humans may contract the plague through bites from these infected fleas.
“Plague can be prevented by avoiding contact with wild rodents, and by keeping pets away from rodent burrows,” public health officials said.
Authorities reported that the CHPD has been observing rodent populations for signs of plague activity in California and working closely with health officials. Video surveillance from 2021 to 2024 in El Dorado County has identified 41 rodents exposed to the plague bacterium. This year, El Dorado County health authorities noted four more rodents in the Tahoe Basin testing positive for the plague.
There are three forms of plague, each presenting different symptoms and arising from various causes. Bubonic plague is the result of flea bites primarily found on rodents.
Authorities said the symptoms of plague will usually show up within two weeks of exposure to an infected animal or flea, and they include fever, nausea, weakness, and swollen lymph nodes. The plague can be treated effectively with antibiotics if symptoms are shown early.
Septicemic plague, which has similar symptoms, can develop from untreated bubonic plague as well as from the handling of infected animals. Should a person with bubonic or septicemic plague go without treatment, and the bacteria reach their lungs, they can develop pneumonic plague. Like other forms of plague, a person infected with pneumonic plague may develop a fever, headache, weakness, and pneumonia, with the latter developing “rapidly.”
While bubonic and septicemic plague may take a few days to set in, the incubation period for pneumonic plague may be just over a day, the CDC reports. It’s the only form that can be spread person-to-person, and it is considered the most serious form of the disease.
El Dorado County health officials did not specify which type of plague the patient had contracted.
Regardless of the type of plague, about 90% of those infected survive with quick treatment. Untreated, “plague is nearly always fatal,” the Cleveland Clinic said.
Infected fleas are largely to blame for plague cases that occur in the U.S. today, but the handling of infected animals like cats, rabbits, rats, mice, and squirrels, according to New York’s Department of Health has also been known to lead to the plague.
Earlier this year, northern Arizona recorded its first pneumonic plague-related death since 2007. Health officials have not said how the Arizona resident became infected. A case of bubonic plague reported in Oregon early last year, the first in the state since 2015, was believed to be brought on by a pet cat. In recent years, Colorado has reported a cat testing positive for septicemic plague and a cat, two prairie dog colonies, and a squirrel testing positive for bubonic plague.
To avoid the plague, health officials advise against feeding squirrels, chipmunks, and other wild rodents. Should you find a sick, injured, or dead rodent, you should not touch it. You should also not let your pets play with or pick up such a rodent.
When camping, officials say you should avoid sleeping or resting near animal burrows or where dead rodents have been spotted. You’ll also want to wear bug spray with DEET on your socks or pant cuffs to reduce flea exposure. If you have to bring your pet into an area where fleas may be present, experts suggest using flea control products.
Cats are highly susceptible to the plague and can, in turn, pose a threat to humans. Should your cat become ill after interacting with a rodent, it’s recommended that you take them to a veterinarian.
If you feel ill after being in an area where plague has occurred, or is known to occur, consult a physician.