Share this @internewscast.com

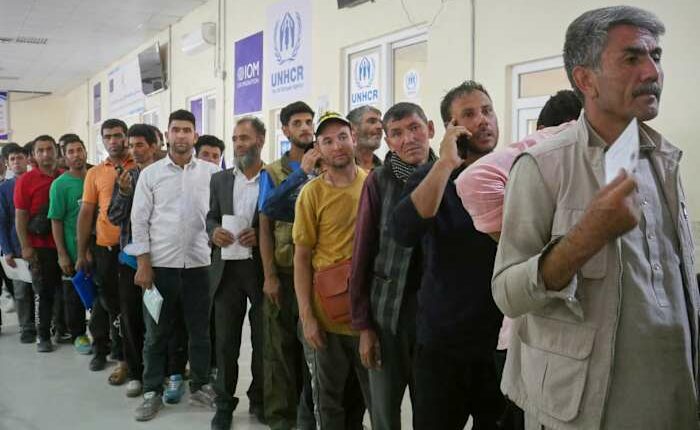
WASHINGTON – As part of the Trump administration’s move to increase eligibility for deportation, temporary provisions allowing nearly 12,000 Afghans to work in the U.S. and preventing their deportation are set to expire on Monday.
The Department of Homeland Security announced in May that it would be terminating Temporary Protected Status (TPS) for 11,700 Afghans in 60 days. This status had enabled them to work and ensured they were not subject to deportation.
The group of Afghans holding TPS is relatively small compared to the approximately 180,000 who have come to the U.S. since the Taliban regained control of Afghanistan in 2021. It remains uncertain how many of the 11,700 individuals covered by TPS have sought or obtained other protective measures, such as asylum, that would prevent their deportation after Monday.
But the removal of the protective status for Afghans has struck a chord with many advocates and volunteers because of the suggestion that it is safe for Afghans — many who helped the U.S. during its two-decade long war there — to go home.
“Since so many of those losing their protections served alongside U.S. forces, we should honor that service by upholding our promise to provide safety and ensure that they have an opportunity to thrive here. We urge Congress to protect Afghans by providing them permanent status – a commitment that is long overdue,” Jennie Murray, President and CEO of the National Immigration Forum, said in a news release Monday.
At the time that Homeland Security Secretary Kristi Noem ended the temporary protected status for Afghans, the department wrote in the decision that the situation in their home country was getting better.
“The Secretary determined that, overall, there are notable improvements in the security and economic situation such that requiring the return of Afghan nationals to Afghanistan does not pose a threat to their personal safety due to armed conflict or extraordinary and temporary conditions,” according to the May announcement.
Temporary Protected Status can be granted by the Homeland Security secretary to people of various nationalities who are in the United States. They can’t be deported and can work legally but they don’t have a pathway to citizenship.
The status is inherently precarious because it is up to the Homeland Security secretary to renew the protections regularly — usually every 18 months. The first Trump administration tried to remove many of these temporary protected statuses but was largely foiled by the courts.
This time around, the Trump administration has moved even more aggressively to remove the protections, thus making more people eligible for removal from the country. The administration has pushed to remove temporary protected status from people from seven countries with Venezuela and Haiti making up the biggest chunk of the hundreds of thousands of people losing their protections.
Critics say that successive administrations essentially rubber-stamped these renewals regardless, and people covered by what’s supposed to be a temporary status end up staying in the United States for years.
CASA, a nonprofit immigrant advocates group, sued the administration over the TPS revocation for Afghans as well as for people from Cameroon – those expire August 4. A federal judge last Friday allowed the lawsuit to go forward but didn’t grant CASA’s request to keep the protections in place while the lawsuit plays out.
Copyright 2025 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without permission.