Share this @internewscast.com

An analysis published on Thursday highlights how climate change, driven by human activity, intensified the fierce winds and heavy rains of Hurricane Melissa. The study also notes that rising temperatures and humidity levels played a critical role in powering the storm.
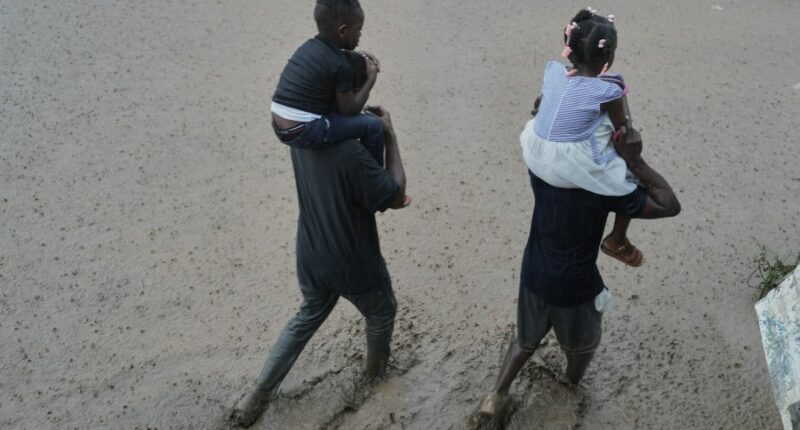
Hurricane Melissa ranks among the most potent Atlantic hurricanes to strike land, wreaking havoc across several Caribbean nations, including Jamaica, Haiti, the Dominican Republic, and Cuba. The storm resulted in numerous casualties and left a trail of destruction, tearing roofs from buildings, damaging hospitals, triggering landslides that blocked roads, and devastating agricultural fields.
Researchers from World Weather Attribution conducted a rapid analysis that revealed climate change amplified Melissa’s top wind speeds by 7% and intensified its rainfall by 16%. Additionally, the analysis indicated that the storm’s development occurred in conditions of temperature and humidity that are now six times more likely due to climate change when compared to pre-industrial times.
Rapid attribution analyses focus on evaluating the factors behind extreme weather events, assessing how such events might differ in a world without the influence of climate change. These studies are typically released shortly after such weather events occur.
As Melissa progressed across the region, it absorbed vast amounts of energy from ocean waters that were unusually warm. The analysis noted that ocean temperatures along Melissa’s route through the Caribbean were approximately 1.4°C (2.5°F) higher than what would be expected in a pre-industrial climate.
Theodore Keeping, a climate scientist with WWA who contributed to the study, explained, “Warmer ocean temperatures essentially fuel a hurricane. The warmer the ocean, the higher the potential wind speeds a hurricane can achieve.”
Melissa is the fourth storm in the Atlantic this year to undergo rapid intensification, which is when a tropical cyclone’s maximum sustained winds increase by at least 30 knots (about 35 mph or 56 kph) in 24 hours.
“A hurricane this rare would actually have had wind speeds about 10 mph (16 kph) less extreme” in a pre-industrial climate, said Keeping. He said research links hurricane wind speeds to economic damage and there would have been less destruction caused by Melissa if the winds were slower.
Scientists have linked rapid intensification of hurricanes in the Atlantic to human-caused climate change. Planet-warming gases released by humans, such as carbon dioxide, cause the atmosphere to hold more water vapor and increase ocean temperatures. Warmer oceans give hurricanes fuel to unleash more rain and strengthen more quickly.
“It’s like basically taking a sponge and wringing it out, and climate change is making that sponge even larger,” said Brian Tang, a professor of atmospheric science at University at Albany.
Tang, who was not involved in the WWA research, said the methodology of the study released Thursday seems robust, and one of the more novel aspects of the analysis was the connection the scientists drew between wind speeds and increase in damage, which he said is a challenging area of research.
Andrew Dessler, professor of atmospheric sciences at Texas A&M University, who was not involved in the WWA research, said the findings of the rapid analysis are in line with existing research about climate change and tropical storms in the Atlantic. “This is completely consistent with our expectation of what’s going to happen in the future,” Dessler said.
Rapid attribution analyses help fill the need for an explanation about the influence of climate change shortly after a catastrophic weather event occurs, said Dessler. He said such analyses are “very valuable as a quick look” before the scientists are able to do more time-consuming calculations.
Dessler said one of the scariest aspects of Melissa was the storm’s peak sustained winds of 185 mph (298 kph) winds. “That’s pretty rare to have a storm that strong. And I think that, to the extent that this is a harbinger of the future, it’s not good,” he said.
___
The Associated Press’ climate and environmental coverage receives financial support from multiple private foundations. AP is solely responsible for all content. Find AP’s standards for working with philanthropies, a list of supporters and funded coverage areas at AP.org.