Share this @internewscast.com
As Australians gear up for a long weekend, severe weather alerts have been issued across the southeastern regions, while Western Australia braces for Tropical Cyclone Luana, set to make landfall this afternoon. Authorities have already closed roads and opened evacuation centers in preparation.
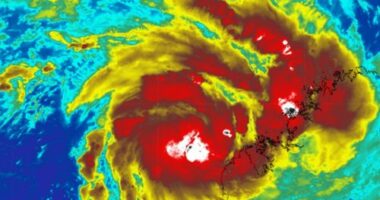
This morning, Tropical Cyclone Luana was officially named as it developed near Broome, located in northwest Western Australia.
Jonathan How, a senior meteorologist at the Bureau of Meteorology (BoM), informed SBS News that the cyclone is on a path toward the Dampier Peninsula. It is predicted to intensify into a Category 2 storm before reaching land today.
“The cyclone will journey across the Dampier Peninsula and proceed to Derby as a Category 1 system tonight, subsequently veering southward,” How explained.
“We’ve already observed increasing winds along this section of the coast, accompanied by a rise in rainfall,” he added.
As a Category 2 cyclone, Luana is expected to unleash fierce winds reaching up to 140 km/h at its core, with outer edges experiencing speeds of about 120 km/h.
It’s the second tropical cyclone in the Kimberly region in a matter of weeks, after Tropical Cyclone Hayley ripped through Broome in late December, hitting a category 4 with wind gusts up to 230 kilometres per hour.
How said while Kimberly residents were likely “accustomed” to cyclone safety practices, he warned holiday-makers to remain “extra alert”.
“Just because it is cyclone season, doesn’t mean people should be complacent,” he said.
“We are also expecting flooding as the cyclone moves further inland. Roads can be cut off, and people could find themselves stranded this holiday season.”
On Saturday morning, roads were closed in Broome and a Watch and Act notice was issued for the Dampier Peninsula. Emergency Services WA urged locals and travellers within the area to reconsider travel plans over the long weekend.
‘Significant and prolonged’ heatwave
BoM has also warned of potentially catastrophic bushfire danger as an intense and long-lasting heatwave drags across NSW, South Australia, Victoria and southern Queensland, with the potential for record-breaking temperatures over the coming week.
“We are seeing a very significant and prolonged heatwave building,” How said.
“It will be the hottest temperatures we have seen since the 2019-20 Black Summer, and we could even see January or even all-time records being broken.
“What will make this heatwave more dangerous is how prolonged it will be. Inland parts of the affected states are likely to see a run of five to seven days in the low to mid, even high 40s.”
On Saturday, Adelaide and Melbourne’s temperatures will soar past 40C, with Adelaide expected to reach 43C. Inland Victoria and NSW will see the mercury nudge the high 40s. Port Augusta, in northern South Australia, is forecast to hit 47C.
While a slight cool change is expected to drop temperatures across Adelaide and Melbourne after next week, it will not reach inland areas, where the severe heat won’t peak until Tuesday or Wednesday.
How said over the week, many south-eastern locations, including parts of NSW and southern Queensland, were also expected to experience temperatures in the mid to high 40s.
“There’s really only some meaningful relief coming through next week, so it is a really long, drawn-out heatwave with increased fire dangers as well,” he said.
While Australians might be accustomed to heat in summer, it was important to exercise caution during extreme temperatures, How warned.
“When we do get these temperatures in the 40s, in some cases dropping to the low-30s overnight, it can put a lot of stress on the body,” he said.
“We’d remind people to drink plenty of water, try to stay out of the heat of the sun, and to of course keep an eye on pets and animals, who might find it more challenging.”
For the latest from SBS News, download our app and subscribe to our newsletter.